Relationship between inflammatory cytokines and cardiorenal anemia syndrome: treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin (rhepo)
- PMID: 18923748
- PMCID: PMC2504408
Relationship between inflammatory cytokines and cardiorenal anemia syndrome: treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin (rhepo)
Abstract
Background and aim: Hemodialysis (HD) patients are exposed to persistent inflammatory state. Erythropoietin resistance is known to be strongly associated with chronic inflammation. Aim of the study was to analyze the effect of elevated inflammatory markers on hemoglobin levels and rhEPO requirements in stable patients of our hemodialysis center.
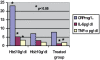
Patients and methods: The study population consisted of 42 patients, 19F/23M, mean age 54.5+/-12.0 years. C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), hemoglobin (Hb), ferritin and left ventricular mass index (LVMi) were recorded. Group 1 consisted of 10 patients with Hb<or=10 g/dl, mean 8.3+/-1.2 g/dl and Group 2, of 10 patients with Hb>or=10 g/dl, mean 12.6+/-1.91 g/dl. None of these 20 patients had been previously treated with rhEPO. Group 3 consisted of 22 patients with mean Hb 10.1+/-1.5 g/dl after treatment with rhEPO.
Results: Group 1 patients had significantly higher IL-6 concentrations than Group 2 (5.21+/-3.94 vs 3.03+/-3.64, p<0.03). Group 3, treated with rhEPO had IL-6 concentrations significantly lower compared to Group 1 (1.15+/-3.81 vs 3.03+/-3.64, p<0.05). HD pts in Group 1 presented significantly higher CRP concentrations compated to pts of Group 2 and 3 (23.1+/-9.1 vs 7.02+/-8.7 and 7.89+/-9.6 respectively, p<0.05). A negative correlation was demonstrated between IL-6 and Hb level (r: 0.33 p<0.05).
Conclusions: A better management of anemia might improve inflammatory state and survival in this population.
Keywords: ESRD; anemia; inflammation; rhEPO requirements.
Figures
References
-
- Hampl H, Riedel E, Scigalla P, Stabell U, Wendel G. Erythropoiesis and erythrocyte age distribution in hemodialysis patients undergoing erythropoietin therapy. Blood Purif. 1990;8:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Besarab A, Bolton WK, Browne JK, et al. The effects of normal as compared with low hematocrit values in patients with cardiac disease who are receiving hemodialysis and epoetin. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:584–590. - PubMed
-
- Sommerburg O, Grune T, Hampl H, Riedel E, Ehrich JH, Siems WG. Does treatment of renal anemia with recombinant erythropietin influence oxidative stress in hemodialysis patients? Clin Nephrol. 2000;53:S23–S29. - PubMed
-
- Jie KE, Verhaar MC, Cramer MJ, et al. Erythropoetin and the cardiorenal syndrome: cellular mechanisms on the cardiorenal connectors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;291:F932–F944. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous