Management of hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic renal failure
- PMID: 18923754
- PMCID: PMC2532962
Management of hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic renal failure
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is recognized as a leading cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal failure. Chronic renal failure is associated with insulin resistance and, in advanced renal failure, decreased insulin degradation. Both of these abnormalities are partially reversed with the institution of dialysis. Except for diet with protein restriction, patients with diabetes should be preferably treated with insulin. The management of the patients with hyperglycemia and chronic renal failure calls for close collaboration between the diabetologist and the nephrologists. This collaboration is very important so that the patient will not be confused and will not lose confidence to the doctors. Furthermore good glycemic control in these patients seems to reduce microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; diabetes; hyperglycemia therapy.
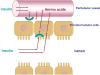
Figures

References
-
- Grundy SM, Howard B, Smith SJr, Eckel R, Redberg R, Bonow RO. Prevention Conference VI: Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: executive summary: conference proceeding for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2002;105:2231–2239. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Serdula MK, Dietz WH, et al. The spread of the obesity epidemic in the United States, 1991-1998. JAMA. 1999;282:1519–1522. - PubMed
-
- USRDS 1999 annual data report. Bethesda, Md: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease; 1999. US Renal Data System; pp. 25–38.
-
- Gerstein HC. Dysglycaemia: a cardiovascular risk factor. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1998;40(Suppl):9–14. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. (UKPDS 33) Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
