Deciphering modular and dynamic behaviors of transcriptional networks
- PMID: 18923925
- PMCID: PMC2276884
- DOI: 10.1007/s11568-007-9004-7
Deciphering modular and dynamic behaviors of transcriptional networks
Abstract
The coordinated and dynamic modulation or interaction of genes or proteins acts as an important mechanism used by a cell in functional regulation. Recent studies have shown that many transcriptional networks exhibit a scale-free topology and hierarchical modular architecture. It has also been shown that transcriptional networks or pathways are dynamic and behave only in certain ways and controlled manners in response to disease development, changing cellular conditions, and different environmental factors. Moreover, evolutionarily conserved and divergent transcriptional modules underline fundamental and species-specific molecular mechanisms controlling disease development or cellular phenotypes. Various computational algorithms have been developed to explore transcriptional networks and modules from gene expression data. In silico studies have also been made to mimic the dynamic behavior of regulatory networks, analyzing how disease or cellular phenotypes arise from the connectivity or networks of genes and their products. Here, we review the recent development in computational biology research on deciphering modular and dynamic behaviors of transcriptional networks, highlighting important findings. We also demonstrate how these computational algorithms can be applied in systems biology studies as on disease, stem cells, and drug discovery.
Figures

 ) from X. At the PSMF stage,
) from X. At the PSMF stage,  is approximated by the product of sparse matrix Y and low-rank Z. The values of all matrices are color coded by using a color heatmap, from dark green (minimum) to dark red (maximum). (Reproduced from (Li et al. 2007b))
is approximated by the product of sparse matrix Y and low-rank Z. The values of all matrices are color coded by using a color heatmap, from dark green (minimum) to dark red (maximum). (Reproduced from (Li et al. 2007b))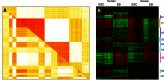
Similar articles
-
Evolutionarily conserved transcriptional co-expression guiding embryonic stem cell differentiation.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003406. Epub 2008 Oct 15. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18923680 Free PMC article.
-
A new multi-scale method to reveal hierarchical modular structures in biological networks.Mol Biosyst. 2016 Nov 15;12(12):3724-3733. doi: 10.1039/c6mb00617e. Mol Biosyst. 2016. PMID: 27783080
-
Hierarchical structure and modules in the Escherichia coli transcriptional regulatory network revealed by a new top-down approach.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Dec 16;5:199. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-199. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15603590 Free PMC article.
-
Modular pharmacology: deciphering the interacting structural organization of the targeted networks.Drug Discov Today. 2013 Jun;18(11-12):560-6. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Drug Discov Today. 2013. PMID: 23353707 Review.
-
Gene regulatory network inference resources: A practical overview.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Jun;1863(6):194430. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.194430. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 31678629 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionarily conserved transcriptional co-expression guiding embryonic stem cell differentiation.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003406. Epub 2008 Oct 15. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18923680 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cyclin B1 and Sec62 as biomarkers for recurrence in patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection.Mol Cancer. 2012 Jun 8;11:39. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-39. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22682366 Free PMC article.
-
Systems genetics of the nuclear factor-κB signal transduction network. I. Detection of several quantitative trait loci potentially relevant to aging.Mech Ageing Dev. 2012 Jan;133(1):11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2011.11.007. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Mech Ageing Dev. 2012. PMID: 22155176 Free PMC article.
-
Modularity in Biological Networks.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 14;12:701331. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.701331. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34594357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling transcriptional regulatory programs by integrative analysis of microarray and transcription factor binding data.Bioinformatics. 2008 Sep 1;24(17):1874-80. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn332. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18586698 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
