Improved MALDI-TOF imaging yields increased protein signals at high molecular mass
- PMID: 18926723
- PMCID: PMC2671225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jasms.2008.09.008
Improved MALDI-TOF imaging yields increased protein signals at high molecular mass
Abstract
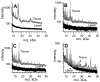
Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrum images are created from an array of mass spectra collected over a tissue surface. We have increased the mass range of proteins that can be detected in tissue sections from kidneys, heart, lung and brain of different rodent species by a modification of the sandwich technique, which involves co-crystallizing matrix with analyte. A tissue section is placed upon a drop of sinapinic acid matrix dissolved in 90% ethanol and 0.5% Triton X-100. Once the matrix has dried, a seed layer of sinapinic crystals is added as a dispersion in xylene. Additional layers of sinapinic acid are added as solutions in 90% ethanol followed by 50% acetonitrile. Numerous peaks with signal to noise ratio of four or greater are observed between 25 kDa to 50 kDa. This represents approximately 10 times as many peaks as are detected using traditional matrix spotting and spraying.
Figures
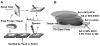




References
-
- Leinweber BD, Monks TJ, Lau SS. The Ethanol Triton X-100 Sandwich Method Yields High Resolution and m/z MALDI Mass Spectral Images on Tissue. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2006;17(5) 1:111S.
-
- Stoeckli M, Farmer TB, Caprioli RM. Automated mass spectrometry imaging with a matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight instrument. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1999;10(1):67–71. - PubMed
-
- Caprioli RM, Farmer TB, Gile J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem. 1997;69(23):4751–60. - PubMed
-
- Chaurand P, Norris JL, Cornett DS, Mobley JA, Caprioli RM. New developments in profiling and imaging of proteins from tissue sections by MALDI mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2006;5(11):2889–900. - PubMed
-
- Chaurand P, Schwartz SA, Reyzer ML, Caprioli RM. Imaging mass spectrometry: principles and potentials. Toxicol Pathol. 2005;33(1):92–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

