DNA cleavage assay for the identification of topoisomerase I inhibitors
- PMID: 18927559
- PMCID: PMC10758284
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2008.174
DNA cleavage assay for the identification of topoisomerase I inhibitors
Abstract
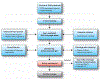
The inhibition of DNA topoisomerase I (Top1) has proven to be a successful approach in the design of anticancer agents. However, despite the clinical successes of the camptothecin derivatives, a significant need for less toxic and more chemically stable Top1 inhibitors still persists. Here, we describe one of the most frequently used protocols to identify novel Top1 inhibitors. These methods use uniquely 3'-radiolabeled DNA substrates and denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to provide evidence for the Top1-mediated DNA cleaving activity of potential Top1 inhibitors. These assays allow comparison of the effectiveness of different drugs in stabilizing the Top1-DNA intermediate or cleavage (cleavable) complex. A variation on these assays is also presented, which provides a suitable system for determining whether the inhibitor blocks the forward cleavage or religation reactions by measuring the reversibility of the drug-induced Top1-DNA cleavage complexes. This entire protocol can be completed in approximately 2 d.
Figures

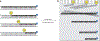

References
-
- Kohlhagen G, Paull K, Cushman M, Nagafufuji P & Pommier Y Protein-linked DNA strand breaks induced by NSC 314622, a non-camptothecin topoisomerase I poison. Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 50–58 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Strumberg D et al. Synthesis of cytotoxic indenoisoquinoline topoisomerase I poisons. J. Med. Chem. 42, 446–457 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Antony S et al. Cellular Topoisomerase I Inhibition and antiproliferative activity by MJ-III-65 (NSC 706744), an indenoisoquinoline topoisomerase I poison. Mol. Pharmacol. 67, 523–530 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Ioanoviciu A et al. Synthesis and mechanism of action studies of a series of norindenoisoquinoline topoisomerase I poisons reveal an inhibitor with a flipped orientation in the ternary DNA-enzyme-inhibitor complex as determined by X-ray crystallographic analysis. J. Med. Chem. 48, 4803–4814 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Staker BL et al. Structures of three classes of anticancer agents bound to the human topoisomerase I-DNA covalent complex. J. Med. Chem. 48, 2336–2345 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

