Biological function and molecular mapping of M antigen in yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum
- PMID: 18927619
- PMCID: PMC2566600
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003449
Biological function and molecular mapping of M antigen in yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum
Abstract
Histoplasmosis, due to the intracellular fungus Histoplasma capsulatum, can be diagnosed by demonstrating the presence of antibodies specific to the immunodominant M antigen. However, the role of this protein in the pathogenesis of histoplasmosis has not been elucidated. We sought to structurally and immunologically characterize the protein, determine yeast cell surface expression, and confirm catalase activity. A 3D-rendering of the M antigen by homology modeling revealed that the structures and domains closely resemble characterized fungal catalases. We generated monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to the protein and determined that the M antigen is present on the yeast cell surface and in cell wall/cell membrane preparations. Similarly, we found that the majority of catalase activity was in extracts containing fungal surface antigens and that the M antigen is not significantly secreted by live yeast cells. The mAbs also identified unique epitopes on the M antigen. The localization of the M antigen to the cell surface of H. capsulatum yeast and the characterization of the protein's major epitopes have important implications since it demonstrates that although the protein may participate in protecting the fungus against oxidative stress it is also accessible to host immune cells and antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
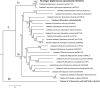

References
-
- Johnson CH, Klotz MG, York JL, Kruft V, McEwen JE. Redundancy, phylogeny and differential expression of Histoplasma capsulatum catalases. Microbiology. 2002;148:1129–1142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

