Rapture of renal angiomyolipoma during pregnancy: a case report
- PMID: 18928528
- PMCID: PMC2576180
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1626-1-245
Rapture of renal angiomyolipoma during pregnancy: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Rapture of a renal angiomyolipoma and massive retroperitoneal hemorrhage, during pregnancy is rare and occasionally fatal. The association of this complication with pregnancy has been reported sporadically in the literature.
Case presentation: We report a case of a 28 years old woman, in 33 week of her first pregnancy who came to our hospital complaining of abdominal pain in the right hemiabdomen, associated with nausea and vomiting. The ultrasound and MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) scan showed a 7 x 7 x 5 cm mass suggestive of angiomyolipoma in the right kidney, with evidence of retroperitoneal bleeding right perirenal and intrarenal haematoma. Given the size of the tumor, presence of symptoms and hemodynamic instability of the patient right nephrectomy was performed, following emergency caesarean delivery. The histological study of the resected mass revealed the presence of angiomyolipoma.
Conclusion: In conclusion, it seems that these tumours show a greater growth index in pregnant women. Angiomyolipoma with spontaneous bleeding during pregnancy is a dangerous condition that may cause mortality in the mother and fetus, but elective, simultaneous cesarean section and radical nephrectomy can be performed. We have also done a review of the literature focusing on its management and its relationship with pregnancy.
Figures

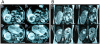

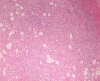
References
-
- Steiner MS, Goldman SM, Fishman EK, Marshall FF. The natural history of renal angiomyolipoma. J Urol. 1993;150:1782–6. - PubMed
-
- Siegel CL, Middleton WD, Teefey SA, McClennan BL. Angiomyolipoma and renal cell carcinoma: US differentiation. Radiology. 1996;198:789–93. - PubMed
-
- Earthman WJ, Mazer MJ, Winfield AC. Angiomyolipomas in tuberous sclerosis: subselective embolotherapy with alcohol, with long-term follow-up study. Radiology. 1986;160:437–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

