Evaluation of a scoring system for assessing prognosis in pediatric acute liver failure
- PMID: 18928939
- PMCID: PMC2581795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.05.013
Evaluation of a scoring system for assessing prognosis in pediatric acute liver failure
Abstract
Background & aims: Pediatric acute liver failure (PALF) results in death or need for liver transplantation (LT) in up to 50% of patients. A scoring system for predicting death or LT (Liver Injury Units [LIU] score) in PALF was previously derived by our group, and used peak values during hospital admission of total bilirubin, prothrombin time/international normalized ratio, and ammonia as significant predictors of outcome. The aims of this study were to test the predictive value of the LIU score in a subsequent validation set of patients and to derive a hospital admission LIU (aLIU) score predictive of outcome.
Methods: Data were obtained from 53 children admitted with PALF from 2002 to 2006. Outcome was defined at 16 weeks as alive without LT, death, or LT.
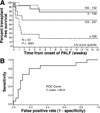
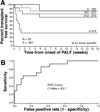
Results: Survival without LT at 16 weeks for each LIU score quartile was 92%, 44%, 60%, and 12%, respectively (P < .001). The receiver operating characteristic C index for predicting death or LT by 4 weeks was 86.3. An admission LIU score was derived using admission total bilirubin and prothrombin time/international normalized ratio. Survival without LT at 16 weeks for each quartile using the aLIU score was 85%, 77%, 69%, and 31% (P = .001). The receiver operating characteristic C index for predicting death or LT by 4 weeks was 83.7.
Conclusions: The original LIU score is a valid predictor of outcome in PALF. The aLIU score is promising and needs to be validated in subsequent patients.
Figures


References
-
- Baker A, Alonso ME, Aw MM, et al. Hepatic failure and liver transplant: Working group report of the Second Work Congress of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. JPGN. 2004;39:S632–S639. - PubMed
-
- Durand P, Debray D, Mandel R, et al. Acute liver failure in infancy: a 14-year experience of a pediatric liver transplantation center. J Pediatr. 2001;139:871–876. - PubMed
-
- Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiødt FV, et al. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(12):947–954. - PubMed
-
- Schiødt FV, Atillasoy E, Shakil AO, et al. Etiology and outome for the 295 patients with acute liver failure in the United States. Liver Transpl Surg. 1999;5(1):29–34. - PubMed

