The complexity of signaling in host-pathogen interactions revealed by the Toxoplasma gondii-dependent modulation of JNK phosphorylation
- PMID: 18929560
- PMCID: PMC2648821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.09.019
The complexity of signaling in host-pathogen interactions revealed by the Toxoplasma gondii-dependent modulation of JNK phosphorylation
Abstract
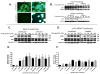
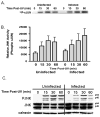
The inhibition of apoptosis by Toxoplasma gondii is governed by its modulation of several signaling cascades including the NFkappaappaB and JNK pathways. This is evident in the dysregulation of JNK activation following treatment with UV and TNFalpha, both apoptogenic stimuli. Infection-mediated interference with the JNK cascade was found to be highly reproducible in HeLa cells. In light of emerging evidence regarding cross talk between the JNK and NFkappaB cascades, we examined the impact of infection in wild type and RelA/p65-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF). Remarkably, parasite infection failed to significantly impact both UV and TNFalpha-mediated JNK phosphorylation in both cell lines suggesting a cell type specific effect. Furthermore siRNA-mediated knockdown of RelA/p65 failed to impact the parasite mediated effects on stimulus dependent activation of JNK in HeLa cells. Finally, the infection mediated suppression of JNK phosphorylation in HeLa cells did not result in decreased JNK kinase activity. Rather, the reduced levels of phospho-JNK in infected cells correlated with increased phosphatase activity noted by the partial rescue of the phenotype following treatment with okadaic acid. Taken together the results indicate that manipulation of the JNK pathway does not involve NFkappaB and is furthermore not a central component of the parasite enforced block of apoptosis. It further highlights the complexity of these systems and the danger of extrapolating results both within and across pathogen-host cell systems based on limited studies.
Figures
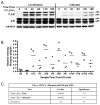
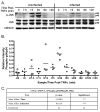
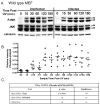

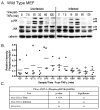


Similar articles
-
Activation of NF-kappaB by Toxoplasma gondii correlates with increased expression of antiapoptotic genes and localization of phosphorylated IkappaB to the parasitophorous vacuole membrane.J Cell Sci. 2003 Nov 1;116(Pt 21):4359-71. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00683. Epub 2003 Sep 9. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12966164
-
Activation of the cellular mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways ERK, P38 and JNK during Toxoplasma gondii invasion.Parasite. 2003 Mar;10(1):59-64. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2003101p59. Parasite. 2003. PMID: 12669350
-
RACK1 mediates activation of JNK by protein kinase C [corrected].Mol Cell. 2005 Aug 5;19(3):309-20. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.025. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16061178 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis and its modulation during infection with Toxoplasma gondii: molecular mechanisms and role in pathogenesis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;289:219-37. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27320-4_10. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15791958 Review.
-
From cells to signaling cascades: manipulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003 Dec 5;39(3):193-203. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00279-7. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14642303 Review.
Cited by
-
The Differential Effect of Toxoplasma Gondii Infection on the Stability of BCL2-Family Members Involves Multiple Activities.Front Microbiol. 2011 Jan 24;2:1. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00001. eCollection 2011. Front Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21716958 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effect of Ursolic Acid as a Novel Toxoplasmosis Inhibitor.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 May 9;11(2):43. doi: 10.3390/ph11020043. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29747388 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Modulates the Host Cell Responses: An Overview of Apoptosis Pathways.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 4;2019:6152489. doi: 10.1155/2019/6152489. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31080827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carmen JC, Hardi L, Sinai AP. Toxoplasma gondii inhibits ultraviolet light-induced apoptosis through multiple interactions with the mitochondrion-dependent programmed cell death pathway. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:301–15. - PubMed
-
- Payne TM, Molestina RE, Sinai AP. Inhibition of caspase activation and a requirement for NF-kappaB function in the Toxoplasma gondii-mediated blockade of host apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:4345–58. - PubMed
-
- Nash PB, Purner MB, Leon RP, Clarke P, Duke RC, Curiel TJ. Toxoplasma gondii-infected cells are resistant to multiple inducers of apoptosis. J Immunol. 1998;160:1824–30. - PubMed
-
- Goebel S, Gross U, Luder CG. Inhibition of host cell apoptosis by Toxoplasma gondii is accompanied by reduced activation of the caspase cascade and alterations of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase expression. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:3495–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

