Robotic partial nephrectomy for renal hilar tumors: a multi-institutional analysis
- PMID: 18930263
- PMCID: PMC2648867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.08.022
Robotic partial nephrectomy for renal hilar tumors: a multi-institutional analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy is an advanced surgical procedure requiring technical skill in minimally invasive techniques. Tumors located adjacent to the renal hilum pose an additional challenge. We report a multi-institutional study of robotic partial nephrectomy for renal hilar tumors and describe our results.
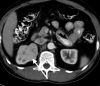
Materials and methods: We evaluated patients from 2 institutions who underwent robotic partial nephrectomy for renal hilar tumors. Renal hilar tumors were defined as tumors abutting the renal artery and/or renal vein on preoperative imaging. After clamping the renal hilar vessels tumors were excised with fine dissection from the renal vessels followed by sutured renal reconstruction.
Results: Robotic partial nephrectomy was successfully performed on 11 patients (mean age 56.4 years, range 30 to 76). Mean tumor size was 3.8 cm (range 2.3 to 6.4). Mean warm ischemia time was 28.9 minutes (range 20 to 39) and mean operating time was 202 minutes (range 154 to 253). Mean blood loss was 220 ml (range 50 to 750). Mean hospital stay was 2.6 days (range 1 to 4). Histopathological evaluation confirmed 8 cases of clear cell renal cell carcinoma, 1 of papillary renal cell carcinoma and 2 of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Surgical margins were negative for malignancy in all cases.
Conclusions: Robotic partial nephrectomy is a safe and feasible approach for select patients with renal hilar tumors. Robotic assistance may facilitate tumor resection and renal reconstruction for challenging renal hilar tumors, offering a minimally invasive and nephron sparing surgical option for select patients who might otherwise require open surgery or total nephrectomy.
Figures




References
-
- Nguyen MM, Gill IS, Ellison LM. The evolving presentation of renal carcinoma in the United States: trends from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. J Urol. 2006;176:2397. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296. - PubMed
-
- Gill IS, Kavoussi LR, Lane BR, Blute ML, Banineau D, Colombo JR, Jr., et al. Comparison of 1,800 laparoscopic and open partial nephrectomies for single renal tumors. J Urol. 2007;178:41. - PubMed
-
- Lane BR, Gill IS. 5-Year outcomes of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. J Urol. 2007;177:70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

