The potential of desferrioxamine-gallium as an anti-Pseudomonas therapeutic agent
- PMID: 18931304
- PMCID: PMC2575493
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808608105
The potential of desferrioxamine-gallium as an anti-Pseudomonas therapeutic agent
Abstract
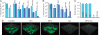
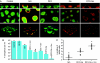
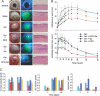
The opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes infections that are difficult to treat by antibiotic therapy. This bacterium can cause biofilm infections where it shows tolerance to antibiotics. Here we report the novel use of a metallo-complex, desferrioxamine-gallium (DFO-Ga) that targets P. aeruginosa iron metabolism. This complex kills free-living bacteria and blocks biofilm formation. A combination of DFO-Ga and the anti-Pseudomonas antibiotic gentamicin caused massive killing of P. aeruginosa cells in mature biofilms. In a P. aeruginosa rabbit corneal infection, topical administration of DFO-Ga together with gentamicin decreased both infiltrate and final scar size by about 50% compared to topical application of gentamicin alone. The use of DFO-Ga as a Trojan horse delivery system that interferes with iron metabolism shows promise as a treatment for P. aeruginosa infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284:1318–1322. - PubMed
-
- O'Toole G, Kaplan HB, Kolter R. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2000;54:49–79. - PubMed
-
- Davies D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:114–122. - PubMed
-
- Rasmussen TB, Givskov M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006;296:149–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

