Phospholipase A2 biochemistry
- PMID: 18931897
- PMCID: PMC2823292
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-008-6132-9
Phospholipase A2 biochemistry
Abstract
The phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) superfamily consists of many different groups of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of the sn-2 ester bond in a variety of different phospholipids. The products of this reaction, a free fatty acid, and lysophospholipid have many different important physiological roles. There are five main types of PLA(2): the secreted sPLA(2)'s, the cytosolic cPLA(2)'s, the Ca(2+)independent iPLA(2)'s, the PAF acetylhydrolases, and the lysosomal PLA(2)'s. This review focuses on the superfamily of PLA(2) enzymes, and then uses three specific examples of these enzymes to examine the differing biochemistry of the three main types of these enzymes. These three examples are the GIA cobra venom PLA(2), the GIVA cytosolic cPLA(2), and the GVIA Ca(2+)-independent iPLA(2).
Figures
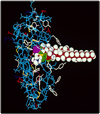

References
-
- Schaloske RH, Dennis EA. The phospholipase A2 superfamily and its group numbering system. BiochimBiophysActa. 2006;1761:1246–1259. - PubMed
-
- Six DA, Dennis EA. The expanding superfamily of phospholipase A(2) enzymes: classification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1488:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Dennis EA. Diversity of group types, regulation, and function of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:13057–13060. - PubMed
-
- Funk CD. Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes: Advances in Eicosanoid Biology. Science. 2001;294:1871–1875. - PubMed
-
- Moolenaar WH, van Meeteren LA, Giepmans BN. The ins and outs of lysophosphatidic acid signaling. Bioessays. 2004;26:870–881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

