Role of the hyperpolarization-activated current Ih in somatosensory neurons
- PMID: 18936078
- PMCID: PMC2655434
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.163154
Role of the hyperpolarization-activated current Ih in somatosensory neurons
Abstract
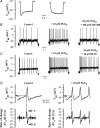
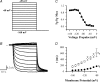
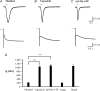
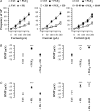
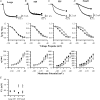
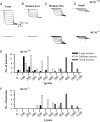
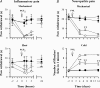
The hyperpolarization-activated current (I(h)) is an inward current activated by hyperpolarization from the resting potential and is an important modulator of action potential firing frequency in many excitable cells. Four hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-modulated subunits, HCN1-4, can form I(h) ion channels. In the present study we investigated the function of I(h) in primary somatosensory neurons. Neuronal firing in response to current injection was promoted by elevating intracellular cAMP levels and inhibited by blockers of I(h), suggesting that I(h) plays a critical role in modulating firing frequency. The properties of I(h) in three size classes of sensory neurons were next investigated. In large neurons I(h) was fast activating and insensitive to elevations in cAMP, consistent with expression of HCN1. I(h) was ablated in most large neurons in HCN1(-/-) mice. In small neurons a slower activating, cAMP-sensitive I(h) was observed, as expected for expression of HCN2 and/or HCN4. Consistent with this, I(h) in small neurons was unchanged in HCN1(-/-) mice. In a neuropathic pain model HCN1(-/-) mice exhibited substantially less cold allodynia than wild-type littermates, suggesting an important role for HCN1 in neuropathic pain. This work shows that I(h) is an important modulator of action potential generation in somatosensory neurons.
Figures


Comment in
-
Funny currents are becoming serious players in nociceptor's sensitization.J Physiol. 2008 Dec 15;586(24):5841-2. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.165852. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 19074817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN. The tetrodotoxinresistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:541–548. - PubMed
-
- Carlton SM, Lekan HA, Kim SH, Chung JM. Behavioral manifestations of an experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by spinal nerve ligation in the primate. Pain. 1994;56:155–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

