AHI-1 interacts with BCR-ABL and modulates BCR-ABL transforming activity and imatinib response of CML stem/progenitor cells
- PMID: 18936234
- PMCID: PMC2571939
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20072316
AHI-1 interacts with BCR-ABL and modulates BCR-ABL transforming activity and imatinib response of CML stem/progenitor cells
Abstract
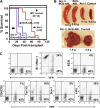
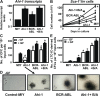
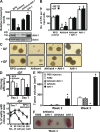
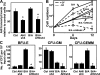
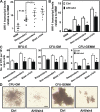
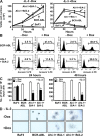
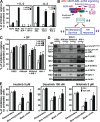
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) represents the first human malignancy successfully treated with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI; imatinib). However, early relapses and the emergence of imatinib-resistant disease are problematic. Evidence suggests that imatinib and other inhibitors may not effectively eradicate leukemic stem/progenitor cells, and that combination therapy directed to complimentary targets may improve treatment. Abelson helper integration site 1 (Ahi-1)/AHI-1 is a novel oncogene that is highly deregulated in CML stem/progenitor cells where levels of BCR-ABL transcripts are also elevated. Here, we demonstrate that overexpression of Ahi-1/AHI-1 in murine and human hematopoietic cells confer growth advantages in vitro and induce leukemia in vivo, enhancing effects of BCR-ABL. Conversely, RNAi-mediated suppression of AHI-1 in BCR-ABL-transduced lin(-)CD34(+) human cord blood cells and primary CML stem/progenitor cells reduces their growth autonomy in vitro. Interestingly, coexpression of Ahi-1 in BCR-ABL-inducible cells reverses growth deficiencies exhibited by BCR-ABL down-regulation and is associated with sustained phosphorylation of BCR-ABL and enhanced activation of JAK2-STAT5. Moreover, we identified an AHI-1-BCR-ABL-JAK2 interaction complex and found that modulation of AHI-1 expression regulates phosphorylation of BCR-ABL and JAK2-STAT5 in CML cells. Importantly, this complex mediates TKI response/resistance of CML stem/progenitor cells. These studies implicate AHI-1 as a potential therapeutic target downstream of BCR-ABL in CML.
Figures


References
-
- Goldman, J.M., and J.V. Melo. 2003. Chronic myeloid leukemia–advances in biology and new approaches to treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 349:1451–1464. - PubMed
-
- Jiang, X., C. Smith, A. Eaves, and C. Eaves. 2007. The challenges of targeting chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Clin. Lymph. Myeloma. 7:S71–S80. - PubMed
-
- Lugo, T.G., A.M. Pendergast, A.J. Muller, and O.N. Witte. 1990. Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of bcr-abl oncogene products. Science. 247:1079–1082. - PubMed
-
- Druker, B.J., S. Tamura, E. Buchdunger, S. Ohno, G.M. Segal, S. Fanning, J. Zimmermann, and N.B. Lydon. 1996. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat. Med. 2:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Sattler, M., and J.D. Griffin. 2003. Molecular mechanisms of transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene. Semin. Hematol. 40:4–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

