Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB 90206
- PMID: 18936475
- PMCID: PMC2651074
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.9847
Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB 90206
Abstract
Purpose: Bevacizumab is an antibody that binds to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and has activity in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Interferon alfa (IFN) is a historic standard first-line treatment for RCC. A prospective, randomized phase III trial of bevacizumab plus IFN versus IFN monotherapy was conducted.
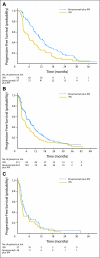
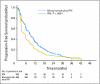
Patients and methods: Patients with previously untreated, metastatic clear-cell RCC were randomly assigned to receive either bevacizumab (10 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks) plus IFN (9 million U subcutaneously three times weekly) or the same dose and schedule of IFN monotherapy in a multicenter phase III trial. The primary end point was overall survival (OS). Secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and safety.
Results: Between October 2003 and July 2005, 732 patients were enrolled. The prespecified stopping rule for OS has not yet been reached. The median PFS was 8.5 months in patients receiving bevacizumab plus IFN (95% CI, 7.5 to 9.7 months) versus 5.2 months (95% CI, 3.1 to 5.6 months) in patients receiving IFN monotherapy (log-rank P < .0001). The adjusted hazard ratio was 0.71 (95% CI, 0.61 to 0.83; P < .0001). Bevacizumab plus IFN had a higher ORR as compared with IFN (25.5% [95% CI, 20.9% to 30.6%] v 13.1% [95% CI, 9.5% to 17.3%]; P < .0001). Overall toxicity was greater for bevacizumab plus IFN, including significantly more grade 3 hypertension (9% v 0%), anorexia (17% v 8%), fatigue (35% v 28%), and proteinuria (13% v 0%).
Conclusion: Bevacizumab plus IFN produces a superior PFS and ORR in untreated patients with metastatic RCC as compared with IFN monotherapy. Toxicity is greater in the combination therapy arm.
Figures

Comment in
-
Targeted Therapies: Bevacizumab and interferon-alpha in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009 May;6(5):253-4. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.45. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19390549
References
-
- Interferon-alpha and survival in metastatic renal carcinoma: Early results of a randomised controlled trial—Medical Research Council Renal Cancer Collaborators. Lancet 353:14-17, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Pyrhönen S, Salminen E, Ruutu M, et al: Prospective randomized trial of interferon alfa-2a plus vinblastine versus vinblastine alone in patients with advanced renal cell cancer. J Clin Oncol 17:2859-2867, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Murphy BA, et al: Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 20:289-296, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Negrier S, Escudier B, Lasset C, et al: Recombinant human interleukin-2, recombinant human interferon alfa-2a, or both in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. Groupe Francais d’Immunotherapie. N Engl J Med 338:1272-1278, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

