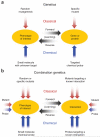
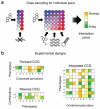
Combination chemical genetics
- PMID: 18936752
- PMCID: PMC2712875
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.120
Combination chemical genetics
Abstract
Predicting the behavior of living organisms is an enormous challenge given their vast complexity. Efforts to model biological systems require large datasets generated by physical binding experiments and perturbation studies. Genetic perturbations have proven important and are greatly facilitated by the advent of comprehensive mutant libraries in model organisms. Small-molecule chemical perturbagens provide a complementary approach, especially for systems that lack mutant libraries, and can easily probe the function of essential genes. Though single chemical or genetic perturbations provide crucial information associating individual components (for example, genes, proteins or small molecules) with pathways or phenotypes, functional relationships between pathways and modules of components are most effectively obtained from combined perturbation experiments. Here we review the current state of and discuss some future directions for 'combination chemical genetics', the systematic application of multiple chemical or mixed chemical and genetic perturbations, both to gain insight into biological systems and to facilitate medical discoveries.
Figures


References
-
- Stelling J, Sauer U, Szallasi Z, Doyle FJ, III, Doyle J. Robustness of cellular functions. Cell. 2004;118:675–685. - PubMed
-
- Koonin EV, Wolf YI, Karev GP. The structure of the protein universe and genome evolution. Nature. 2002;420:218–223. - PubMed
-
- Hood L, Heath JR, Phelps ME, Lin B. Systems biology and new technologies enable predictive and preventative medicine. Science. 2004;306:640–643. - PubMed
-
- Davidson EH, et al. A genomic regulatory network for development. Science. 2002;295:1669–1678. - PubMed
-
- Silva JM, et al. Second-generation shRNA libraries covering the mouse and human genomes. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:1281–1288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

