New developments in mast cell biology
- PMID: 18936782
- PMCID: PMC2856637
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.f.216
New developments in mast cell biology
Abstract
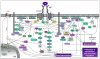
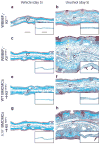
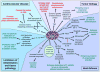
Mast cells can function as effector and immunoregulatory cells in immunoglobulin E-associated allergic disorders, as well as in certain innate and adaptive immune responses. This review focuses on exciting new developments in the field of mast cell biology published in the past year. We highlight advances in the understanding of FcvarepsilonRI-mediated signaling and mast cell-activation events, as well as in the use of genetic models to study mast cell function in vivo. Finally, we discuss newly identified functions for mast cells or individual mast cell products, such as proteases and interleukin 10, in host defense, cardiovascular disease and tumor biology and in settings in which mast cells have anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive functions.
Figures

References
-
- Kitamura Y. Heterogeneity of mast cells and phenotypic change between subpopulations. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:59–76. - PubMed
-
- Mekori YA, Metcalfe DD. Mast cells in innate immunity. Immunol Rev. 2000;173:131–40. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami T, Galli SJ. Regulation of mast-cell and basophil function and survival by IgE. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:773–86. - PubMed
-
- Marone G, Galli SJ, Kitamura Y. Probing the roles of mast cells and basophils in natural and acquired immunity, physiology and disease. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:425–7. - PubMed
-
- Metz M, Grimbaldeston MA, Nakae S, Piliponsky AM, Tsai M, Galli SJ. Mast cells in the promotion and limitation of chronic inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2007;217:304–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

