Nanocrystal core high-density lipoproteins: a multimodality contrast agent platform
- PMID: 18939808
- PMCID: PMC2629801
- DOI: 10.1021/nl801958b
Nanocrystal core high-density lipoproteins: a multimodality contrast agent platform
Abstract
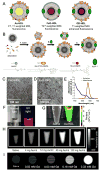
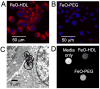
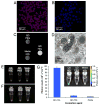
High density lipoprotein (HDL) is an important natural nanoparticle that may be modified for biomedical imaging purposes. Here we developed a novel technique to create unique multimodality HDL mimicking nanoparticles by incorporation of gold, iron oxide, or quantum dot nanocrystals for computed tomography, magnetic resonance, and fluorescence imaging, respectively. By including additional labels in the corona of the particles, they were made multifunctional. The characteristics of these nanoparticles, as well as their in vitro and in vivo behavior, revealed that they closely mimic native HDL.
Figures


Comment in
- Nano Lett. 4:7.
References
-
- Mulder WJM, Cormode DP, Hak S, Lobatto ME, Silvera S, Fayad ZA. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008;5:S103–S111. - PubMed
-
- Kim D, Park S, Lee JH, Jeong YY, Jon S. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:7661–7665. - PubMed
-
- El-Sayed IH, Huang X, El-Sayed MA. Nano Lett. 2005;5:829–834. - PubMed
-
- Jaffer FA, Libby P, Weissleder R. Circulation. 2007;116:1052–1061. - PubMed
-
- de Vries IJM, Lesterhuis WJ, Barentsz JO, Verdijk P, van Krieken JH, Boerman OC, Oyen WJG, Bonenkamp JJ, Boezeman JB, Adema GJ, Bulte JWM, Scheenen TWJ, Punt CJA, Heerschap A, Figdor CG. Nature Biotechnology. 2005;23:1407–1413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

