Motivations and methods for analyzing pulsatile hormone secretion
- PMID: 18940916
- PMCID: PMC2647703
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2008-0005
Motivations and methods for analyzing pulsatile hormone secretion
Abstract
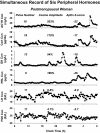
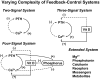
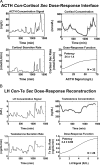
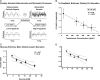
Endocrine glands communicate with remote target cells via a mixture of continuous and intermittent signal exchange. Continuous signaling allows slowly varying control, whereas intermittency permits large rapid adjustments. The control systems that mediate such homeostatic corrections operate in a species-, gender-, age-, and context-selective fashion. Significant progress has been made in understanding mechanisms of adaptive interglandular signaling in vivo. Principal goals are to understand the physiological origins, significance, and mechanisms of pulsatile hormone secretion. Key analytical issues are: 1) to quantify the number, size, shape, and uniformity of pulses, nonpulsatile (basal) secretion, and elimination kinetics; 2) to evaluate regulation of the axis as a whole; and 3) to reconstruct dose-response interactions without disrupting hormone connections. This review will focus on the motivations driving and the methodologies used for such analyses.
Figures












References
-
- Urban RJ, Evans WS, Rogol AD, Kaiser DL, Johnson ML, Veldhuis JD 1988 Contemporary aspects of discrete peak detection algorithms. I. The paradigm of the luteinizing hormone pulse signal in men. Endocr Rev 9:3–37 - PubMed
-
- Evans WS, Sollenberger MJ, Booth Jr RA, Rogol AD, Urban RJ, Carlsen EC, Johnson ML, Veldhuis JD 1992 Contemporary aspects of discrete peak detection algorithms. II. The paradigm of the luteinizing hormone pulse signal in women. Endocr Rev 13:81–104 - PubMed
-
- Giustina A, Veldhuis JD 1998 Pathophysiology of the neuroregulation of growth hormone secretion in experimental animals and the human. Endocr Rev 19:717–797 - PubMed
-
- Veldhuis JD, Roemmich JN, Richmond EJ, Bowers CY 2006 Somatotropic and gonadotropic axes linkages in infancy, childhood, and the puberty-adult transition. Endocr Rev 27:101–140 - PubMed
-
- Keenan DM, Veldhuis JD 2003 Mathematical modeling of receptor-mediated interlinked systems. Encyclopedia of hormones. San Diego: Academic Press; 286–294
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG023133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AG29362/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019695/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NIA AG019695/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG29215/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG23777/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG029215/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AG23133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG029362/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG023777/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG019695/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073148/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK73148/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

