Role of HAMP domains in chemotaxis signaling by bacterial chemoreceptors
- PMID: 18940922
- PMCID: PMC2570609
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806401105
Role of HAMP domains in chemotaxis signaling by bacterial chemoreceptors
Abstract
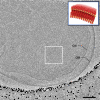
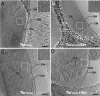
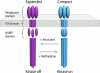
Bacterial chemoreceptors undergo conformational changes in response to variations in the concentration of extracellular ligands. These changes in chemoreceptor structure initiate a series of signaling events that ultimately result in regulation of rotation of the flagellar motor. Here we have used cryo-electron tomography combined with 3D averaging to determine the in situ structure of chemoreceptor assemblies in Escherichia coli cells that have been engineered to overproduce the serine chemoreceptor Tsr. We demonstrate that chemoreceptors are organized as trimers of receptor dimers and display two distinct conformations that differ principally in arrangement of the HAMP domains within each trimer. Ligand binding and methylation alter the distribution of chemoreceptors between the two conformations, with serine binding favoring the "expanded" conformation and chemoreceptor methylation favoring the "compact" conformation. The distinct positions of chemoreceptor HAMP domains within the context of a trimeric unit are thus likely to represent important aspects of chemoreceptor structural changes relevant to chemotaxis signaling. Based on these results, we propose that the compact and expanded conformations represent the "kinase-on" and "kinase-off" states of chemoreceptor trimers, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wadhams GH, Armitage JP. Making sense of it all: Bacterial chemotaxis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:1024–1037. - PubMed
-
- Webre DJ, Wolanin PM, Stock JB. Modulated receptor interactions in bacterial transmembrane signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:478–482. - PubMed
-
- Studdert CA, Parkinson JS. In vivo crosslinking methods for analyzing the assembly and architecture of chemoreceptor arrays. Methods Enzymol. 2007;423:414–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

