Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism
- PMID: 18940959
- PMCID: PMC2948812
- DOI: 10.1093/alcalc/agn079
Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism
Abstract
Aims: This is a review of preclinical studies covering alcohol-induced brain neuronal death and loss of neurogenesis as well as abstinence-induced brain cell genesis, e.g. brain regeneration. Efforts are made to relate preclinical studies to human studies.
Methods: The studies described are preclinical rat experiments using a 4-day binge ethanol treatment known to induce physical dependence to ethanol. Neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits following binge treatment mimic the mild degeneration and cognitive deficits found in humans. Various histological methods are used to follow brain regional degeneration and regeneration.
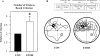
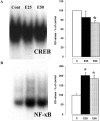
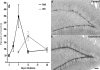
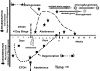
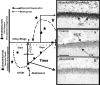
Results: Alcohol-induced degeneration occurs due to neuronal death during alcohol intoxication. Neuronal death is related to increases in oxidative stress in brain that coincide with the induction of proinflammatory cytokines and oxidative enzymes that insult brain. Degeneration is associated with increased NF-kappaB proinflammatory transcription and decreased CREB transcription. Corticolimbic brain regions are most sensitive to binge-induced degeneration and induce relearning deficits. Drugs that block oxidative stress and NF-kappaB transcription or increase CREB transcription block binge-induced neurodegeneration, inhibition of neurogenesis and proinflammatory enzyme induction. Regeneration of brain occurs during abstinence following binge ethanol treatment. Bursts of proliferating cells occur across multiple brain regions, with many new microglia across brain after months of abstinence and many new neurons in neurogenic hippocampal dentate gyrus. Brain regeneration may be important to sustain abstinence in humans.
Conclusions: Alcohol-induced neurodegeneration occurs primarily during intoxication and is related to increased oxidative stress and proinflammatory proteins that are neurotoxic. Abstinence after binge ethanol intoxication results in brain cell genesis that could contribute to the return of brain function and structure found in abstinent humans.
Figures
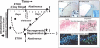


Similar articles
-
Microglial activation is not equivalent to neuroinflammation in alcohol-induced neurodegeneration: The importance of microglia phenotype.Neurobiol Dis. 2013 Jun;54:239-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.12.016. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Neurobiol Dis. 2013. PMID: 23313316 Free PMC article.
-
BHT blocks NF-kappaB activation and ethanol-induced brain damage.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006 Nov;30(11):1938-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00239.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006. PMID: 17067360
-
Alcohol and adult neurogenesis: roles in neurodegeneration and recovery in chronic alcoholism.Hippocampus. 2006;16(3):287-95. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20162. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 16421863 Review.
-
Neuronal degeneration in rat cerebrocortical and olfactory regions during subchronic "binge" intoxication with ethanol: possible explanation for olfactory deficits in alcoholics.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996 Apr;20(2):284-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb01641.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996. PMID: 8730219
-
Role of microglia in ethanol-induced neurodegenerative disease: Pathological and behavioral dysfunction at different developmental stages.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Dec;144(3):321-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.07.002. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25017304 Review.
Cited by
-
Microglial activation is not equivalent to neuroinflammation in alcohol-induced neurodegeneration: The importance of microglia phenotype.Neurobiol Dis. 2013 Jun;54:239-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.12.016. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Neurobiol Dis. 2013. PMID: 23313316 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Developing Brain.Brain Sci. 2016 Aug 16;6(3):31. doi: 10.3390/brainsci6030031. Brain Sci. 2016. PMID: 27537918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High mobility group box 1/Toll-like receptor danger signaling increases brain neuroimmune activation in alcohol dependence.Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Apr 1;73(7):602-12. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.09.030. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23206318 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanins protect against ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis via GABAB1 receptors intracellular signaling in prenatal rat hippocampal neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;48(1):257-69. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8458-y. Epub 2013 May 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23645118
-
Functional Activation of Newborn Neurons Following Alcohol-Induced Reactive Neurogenesis.Brain Sci. 2021 Apr 15;11(4):499. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11040499. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124:319–35. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong RJ, Barker RA. Neurodegeneration: a failure of neuroregeneration? Lancet. 2001;358:1174–6. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA. Blood–brain barrier transport of cytokines: a mechanism for neuropathology. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:973–84. - PubMed
-
- Baydas G, Tuzcu M. Protective effects of melatonin against ethanol-induced reactive gliosis in hippocampus and cortex of young and aged rats. Exp Neurol. 2005;194:175–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

