Properties and structure-function relationships of veltuzumab (hA20), a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody
- PMID: 18941114
- PMCID: PMC2635072
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-168146
Properties and structure-function relationships of veltuzumab (hA20), a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody
Erratum in
- Blood. 2009 May 21;113(21):5368
Abstract
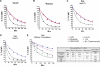
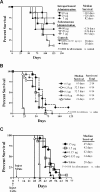
Veltuzumab is a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody with complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) identical to rituximab, except for one residue at the 101st position (Kabat numbering) in CDR3 of the variable heavy chain (V(H)), having aspartic acid (Asp) instead of asparagine (Asn), with framework regions of epratuzumab, a humanized anti-CD22 antibody. When compared with rituximab, veltuzumab has significantly reduced off-rates in 3 human lymphoma cell lines tested, as well as increased complement-dependent cytotoxicity in 1 of 3 cell lines, but no other in vitro differences. Mutation studies confirmed that the differentiation of the off-rate between veltuzumab and rituximab is related to the single amino acid change in CDR3-V(H). Studies of intraperitoneal and subcutaneous doses in mouse models of human lymphoma and in normal cynomolgus monkeys disclosed that low doses of veltuzumab control tumor growth or deplete circulating or sessile B cells. Low- and high-dose veltuzumab were significantly more effective in vivo than rituximab in 3 lymphoma models. These findings are consistent with activity in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma given low intravenous or subcutaneous doses of veltuzumab. Thus, changing Asn(101) to Asp(101) in CDR3-V(H) of rituximab is responsible for veltuzumab's lower off-rate and apparent improved potency in preclinical models that could translate into advantages in patients.
Figures
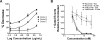

References
-
- Sharkey RM, Goldenberg DM. Targeted therapy of cancer: new prospects for antibodies and immunoconjugates. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:226–243. - PubMed
-
- Castillo J, Winer E, Quesenberry P. Newer monoclonal antibodies for hematological malignancies. Exp Hematol. 2008;36:755–768. - PubMed
-
- Stein R, Qu Z, Chen S, et al. Characterization of a new humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. IMMU-106, and its use in combination with the humanized anti-CD22 antibody, epratuzumab, for the therapy of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:2868–2878. - PubMed
-
- Teeling JL, French RR, Cragg MS, et al. Characterization of new human CD20 monoclonal antibodies with potent cytolytic activity against non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2004;104:1793–1800. - PubMed
-
- Vugmeyster Y, Beyer J, Howell K, et al. Depletion of B cells by a humanized anti-CD20 antibody PRO70769 in Macaca fascicularis. J Immunother. 2005;28:212–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

