Nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase: an exposure biomarker of organophosphate pesticides and nerve agents
- PMID: 18942695
- PMCID: PMC2909471
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.200800412
Nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase: an exposure biomarker of organophosphate pesticides and nerve agents
Abstract
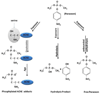
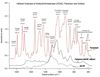
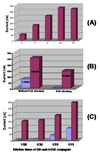
A nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor has been developed for the detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which is a potential biomarker of exposure to organophosphate (OP) pesticides and chemical warfare nerve agents. Zirconia nanoparticles (ZrO(2) NPs) were used as selective sorbents to capture the phosphorylated AChE adduct, and quantum dots (ZnS@CdS, QDs) were used as tags to label monoclonal anti-AChE antibody to quantify the immunorecognition events. The sandwich-like immunoreactions were performed among the ZrO(2) NPs, which were pre-coated on a screen printed electrode (SPE) by electrodeposition, phosphorylated AChE and QD-anti-AChE. The captured QD tags were determined on the SPE by electrochemical stripping analysis of its metallic component (cadmium) after an acid-dissolution step. Paraoxon was used as the model OP insecticide to prepare the phosphorylated AChE adducts to demonstrate proof of principle for the sensor. The phosphorylated AChE adduct was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and mass spectroscopy. The binding affinity of anti-AChE to the phosphorylated AChE was validated with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The parameters (e.g., amount of ZrO(2) NP, QD-anti-AChE concentration,) that govern the electrochemical response of immunosensors were optimized. The voltammetric response of the immunosensor is highly linear over the range of 10 pM to 4 nM phosphorylated AChE, and the limit of detection is estimated to be 8.0 pM. The immunosensor also successfully detected phosphorylated AChE in human plasma. This new nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor provides an opportunity to develop field-deployable, sensitive, and quantitative biosensors for monitoring exposure to a variety of OP pesticides and nerve agents.
Figures

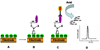
Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic test strip with fluorescent detector for quantification of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase: an exposure biomarker of organophosphorus agents.Analyst. 2013 Sep 21;138(18):5431-6. doi: 10.1039/c3an00621b. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Analyst. 2013. PMID: 23885349
-
Nanoparticle-based immunosensor with apoferritin templated metallic phosphate label for quantification of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase.Biosens Bioelectron. 2011 May 15;26(9):3857-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.02.047. Epub 2011 Mar 5. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011. PMID: 21481580
-
Magnetic electrochemical immunoassays with quantum dot labels for detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase in plasma.Anal Chem. 2008 Nov 15;80(22):8477-84. doi: 10.1021/ac801211s. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Anal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18855408 Free PMC article.
-
SAR study to find optimal cholinesterase reactivator against organophosphorous nerve agents and pesticides.Arch Toxicol. 2016 Dec;90(12):2831-2859. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1827-3. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Arch Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27582056 Review.
-
Organophosphorus pesticides: do they all have the same mechanism of toxicity?J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 1999 Apr-Jun;2(2):161-81. doi: 10.1080/109374099281205. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 1999. PMID: 10230392 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous detection of dual biomarkers from humans exposed to organophosphorus pesticides by combination of immunochromatographic test strip and ellman assay.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 May 1;104:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.12.029. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29306031 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Nanosensor/Smartphone Platform for Point-of-Care Biomonitoring of Human Exposure to Pesticides.Anal Chem. 2025 May 13;97(18):9701-9712. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c06421. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40279400 Free PMC article.
-
Portable Nanoparticle-Based Sensors for Food Safety Assessment.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Dec 5;15(12):30736-58. doi: 10.3390/s151229826. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26690169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Fluidics-Based Biosensor to Detect and Characterize Inhibition Patterns of Organophosphate to Acetylcholinesterase in Food Materials.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Apr 3;12(4):397. doi: 10.3390/mi12040397. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916863 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials - acetylcholinesterase enzyme matrices for organophosphorus pesticides electrochemical sensors: a review.Sensors (Basel). 2009;9(6):4034-55. doi: 10.3390/s90604034. Epub 2009 May 26. Sensors (Basel). 2009. PMID: 22408512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenberry TL. Advances in enzymology and related areas of molecular biology. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1975.
-
- Zhang S, Zhao H, John R. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001;16:1119–1126. - PubMed
-
- Fennouh S, Casimiri V, Burstein C. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1997;12:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Cremisini C, Disario S, Mela J, Pilloton R, Palleschi G. Anal. Chim Acta. 1995;311:273–280.
-
- Guerrieri A, Monaci L, Quinto M, Palmisano F. Analyst. 2002;127:5–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

