Kinetics and mechanism of inhibition of a serine beta-lactamase by O-aryloxycarbonyl hydroxamates
- PMID: 18942857
- PMCID: PMC2669106
- DOI: 10.1021/bi8015247
Kinetics and mechanism of inhibition of a serine beta-lactamase by O-aryloxycarbonyl hydroxamates
Abstract
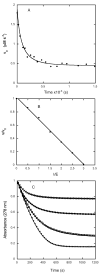
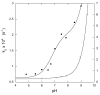
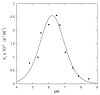
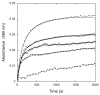
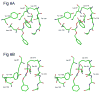
The class C serine beta-lactamase of Enterobacter cloacae P99 is irreversibly inhibited by O-aryloxycarbonyl hydroxamates. A series of these new inhibitors has been prepared to investigate the kinetics and mechanism of the inactivation reaction. A pH-rate profile for the reaction indicated that the reactive form of the inhibitor is neutral rather than anionic. The reaction rate is enhanced by electron-withdrawing aryloxy substituents and by hydrophobic substitution on both aryloxy and hydroxamate groups. Kinetics studies show that the rates of loss of the two possible leaving groups, aryloxide and hydroxamate, are essentially the same as the rate of enzyme inactivation. Nucleophilic trapping experiments prove, however, that the aryl oxide is the first to leave. It is likely, therefore, that the rate-determining step of inactivation is the initial acylation reaction, most likely of the active site serine, yielding a hydroxamoyl-enzyme intermediate. This then partitions between hydrolysis and aminolysis by Lys 315, the latter to form an inactive, cross-linked active site. A previously described crystal structure of the inactivated enzyme shows a carbamate cross-link of Ser 64 and Lys 315. Structure-activity studies of the reported compounds suggest that they do not react at the enzyme active site in the same way as normal substrates. In particular, it appears that the initial acylation by these compounds does not involve the oxyanion hole, an unprecedented departure from known and presumed reactivity. Molecular modeling suggests that an alternative oxyanion hole may have been recruited, consisting of the side chain functional groups of Tyr 150 and Lys 315. Such an alternative mode of reaction may lead to the design of novel inhibitors.
Figures

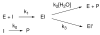
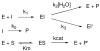
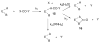

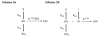

References
-
- Abraham EP. The beta-lactam antibiotics. Sci Am. 1981;244:76–86. - PubMed
-
- Jacoby G, Bush K. β-Lactam resistance in the 21st century. In: White DG, Alekshun MN, McDermott PF, editors. Frontiers in Antimicrobial Resistance. Am. Soc. Microbiol; Washington, D.C: 2005. pp. 53–65.
-
- Fisher JF, Meroueh SA, Mobashery S. Bacterial resistance to β-lactam antibiotics: compelling opportunism, compelling opportunity. Chem Rev. 2005;105:395–424. - PubMed
-
- Buynak JD. Understanding the longevity of the β-lactam antibiotics and of antibiotic/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;71:930–940. - PubMed
-
- Babic M, Hujer AM, Bonomo RA. What’s new in antibiotic resistance? Focus on beta-lactamases. Drug Resist Updates. 2006;9:142–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

