Schizophrenia-related neural and behavioral phenotypes in transgenic mice expressing truncated Disc1
- PMID: 18945897
- PMCID: PMC6671369
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3299-08.2008
Schizophrenia-related neural and behavioral phenotypes in transgenic mice expressing truncated Disc1
Abstract
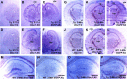
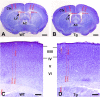
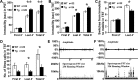
Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 (DISC1), identified by positional cloning of a balanced translocation (1;11) with the breakpoint in intron 8 of a large Scottish pedigree, is associated with a range of neuropsychiatric disorders including schizophrenia. To model this mutation in mice, we have generated Disc1(tr) transgenic mice expressing 2 copies of truncated Disc1 encoding the first 8 exons using a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC). With this partial simulation of the human situation, we have discovered a range of phenotypes including a series of novel features not previously reported. Disc1(tr) transgenic mice display enlarged lateral ventricles, reduced cerebral cortex, partial agenesis of the corpus callosum, and thinning of layers II/III with reduced neural proliferation at midneurogenesis. Parvalbumin GABAergic neurons are reduced in the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex, and displaced in the dorsolateral frontal cortex. In culture, transgenic neurons grow fewer and shorter neurites. Behaviorally, transgenic mice exhibit increased immobility and reduced vocalization in depression-related tests, and impairment in conditioning of latent inhibition. These abnormalities in Disc1(tr) transgenic mice are consistent with findings in severe schizophrenia.
Figures







References
-
- Assadi AH, Zhang G, Beffert U, McNeil RS, Renfro AL, Niu S, Quattrocchi CC, Antalffy BA, Sheldon M, Armstrong DD, Wynshaw-Boris A, Herz J, D'Arcangelo G, Clark GD. Interaction of reelin signaling and Lis1 in brain development. Nat Genet. 2003;35:270–276. - PubMed
-
- Braff DL, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR. Human studies of prepulse inhibition of startle: normal subjects, patient groups, and pharmacological studies. Psychopharmacology. 2001;156:234–258. - PubMed
-
- Brandon NJ, Handford EJ, Schurov I, Rain JC, Pelling M, Duran-Jimeniz B, Camargo LM, Oliver KR, Beher D, Shearman MS, Whiting PJ. Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 and Nudel form a neurodevelopmentally regulated protein complex: implications for schizophrenia and other major neurological disorders. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;25:42–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
