Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes
- PMID: 18945920
- PMCID: PMC2606813
- DOI: 10.2337/dc08-9025
Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes
Abstract
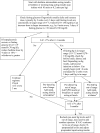
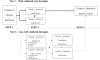
The consensus algorithm for the medical management of type 2 diabetes was published in August 2006 with the expectation that it would be updated, based on the availability of new interventions and new evidence to establish their clinical role. The authors continue to endorse the principles used to develop the algorithm and its major features. We are sensitive to the risks of changing the algorithm cavalierly or too frequently, without compelling new information. An update to the consensus algorithm published in January 2008 specifically addressed safety issues surrounding the thiazolidinediones. In this revision, we focus on the new classes of medications that now have more clinical data and experience.
Figures
Comment in
-
Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes: response to Nathan et al.Diabetes Care. 2009 Mar;32(3):e34; author reply e37-8. doi: 10.2337/dc08-2093. Diabetes Care. 2009. PMID: 19246585 No abstract available.
-
Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes: response to Nathan et al.Diabetes Care. 2009 Mar;32(3):e35-6; author reply e37-8. doi: 10.2337/dc08-2275. Diabetes Care. 2009. PMID: 19246586 No abstract available.
-
Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Response to Nathan et al.Diabetes Care. 2009 May;32(5):e58; author rely e59. doi: 10.2337/dc09-0125. Diabetes Care. 2009. PMID: 19407068 No abstract available.
-
A practice-based approach to the 2012 position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2013 Jul;29(7):793-9. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.798637. Epub 2013 May 10. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013. PMID: 23614630
References
-
- American Diabetes Association: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2008 (Position Statement). Diabetes Care 31(Suppl. 1):S12–S54, 2008 - PubMed
-
- European Diabetes Policy Group: A desk-top guide to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 16:716–730, 1999 - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence: Clinical guidelines for type 2 diabetes mellitus: management of blood glucose [article online], 2002. Available from http://www.nice.org.uk./Guidancet/CG66
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group: The effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. N Engl J Med 329:978–986, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Reichard P, Nilsson B-Y, Rosenqvist U: The effect of long-term intensified insulin treatment on the development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:304–309, 1993 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

