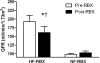Effect of protein kinase Cbeta inhibition on renal hemodynamic function and urinary biomarkers in humans with type 1 diabetes: a pilot study
- PMID: 18945921
- PMCID: PMC2606837
- DOI: 10.2337/dc08-1609
Effect of protein kinase Cbeta inhibition on renal hemodynamic function and urinary biomarkers in humans with type 1 diabetes: a pilot study
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to examine the effect of protein kinase Cbeta inhibition with ruboxistaurin on renal hemodynamic function and urinary biomarkers (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 [MCP-1] and epidermal growth factor) in renin angiotensin system blockade-treated type 1 diabetic subjects.
Research design and methods: Albuminuric subjects were randomized (2:1) to ruboxistaurin (32 mg daily; n = 13) or placebo (n = 7) for 8 weeks. Renal hemodynamic function was measured during clamped euglycemia or hyperglycemia and before and after ruboxistaurin or placebo.
Results: Ruboxistaurin was not associated with between-group differences during clamped euglycemia or hyperglycemia. In a post hoc analysis comparing hyperfilterers with normofilterers during euglycemia, glomerular filtration rate and MCP-1 decreased, whereas the epidermal growth factor-to-MCP-1 ratio increased in hyperfilterers versus normofilterers (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The effect of ruboxistaurin is modest and dependent, at least in part, on the level of ambient glycemia and baseline glomerular filtration rate.
Figures
References
-
- Ishii H, Koya D, King GL: Protein kinase C activation and its role in the development of vascular complications in diabetes mellitus. J Mol Med 76:21–31, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Ishii H, Jirousek MR, Koya D, Takagi C, Xia P, Clermont A, Bursell SE, Kern TS, Ballas LM, Heath WF, Stramm LE, Feener EP, King GL: Amelioration of vascular dysfunctions in diabetic rats by an oral PKC beta inhibitor. Science 272:728–731, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Gilbert RE, Cox A, McNally PG, Wu LL, Dziadek M, Cooper ME, Jerums G: Increased epidermal growth factor in experimental diabetes related kidney growth in rats. Diabetologia 40:778–785, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Tuttle KR: Linking metabolism and immunology: diabetic nephropathy is an inflammatory disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1537–1538, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Giunti S, Tesch GH, Pinach S, Burt DJ, Cooper ME, Cavallo-Perin P, Camussi G, Gruden G: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 has prosclerotic effects both in a mouse model of experimental diabetes and in vitro in human mesangial cells. Diabetologia 51:198–207, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous