Comparison of once- versus twice-daily administration of insulin detemir, used with mealtime insulin aspart, in basal-bolus therapy for type 1 diabetes: assessment of detemir administration in a progressive treat-to-target trial (ADAPT)
- PMID: 18945928
- PMCID: PMC2606825
- DOI: 10.2337/dc08-0332
Comparison of once- versus twice-daily administration of insulin detemir, used with mealtime insulin aspart, in basal-bolus therapy for type 1 diabetes: assessment of detemir administration in a progressive treat-to-target trial (ADAPT)
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare effects of insulin detemir once daily versus twice a day in a basal-bolus insulin regimen.
Research design and methods: In this open-label, 7-month study, 520 patients with type 1 diabetes were randomly assigned to receive detemir once daily or twice daily with mealtime insulin aspart. Insulin doses were titrated over 1 month, with patients followed up over the subsequent 3 months. Thereafter, patients were able to switch from one regimen to the other, with an additional nonrandomized 3-month follow-up, to a total of 7 months. The primary end point was A1C at 4 months, with noninferiority defined as a difference <0.4% between groups.
Results: A1C at 4 months was 8.1 +/- 0.9 versus 8.0 +/- 1.0% with once- and twice-daily detemir, respectively, with an adjusted between-group difference of 0.12% (95% CI -0.01 to 0.25%), showing noninferiority for once-daily dosing. Similar results were found in the per protocol population. Improvement in A1C was similar in both groups (-0.4 +/- 0.8 vs. -0.5 +/- 0.8%; P = 0.09, NS) but with differences in the 7-point glucose profile. Detemir doses were lower (29 +/- 18 vs. 39 +/- 20 units/day, P < 0.001), but aspart doses were higher (34 +/- 17 vs. 26 +/- 14 IU/day, P < 0.001) with once-daily detemir. At 7 months, A1C decreased slightly in patients switched from once-daily to twice-daily administration (8.2 +/- 0.8 vs. 8.0 +/- 0.8%; P = 0.34, NS) in association with increased total insulin doses (P < 0.05), but A1C increased in those switched from twice-daily to once-daily administration (7.2 +/- 0.9 vs. 7.6 +/- 0.8%, P < 0.05) in association with decreased doses (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Although some individuals may benefit from twice-daily dosing, the most suitable routine starting schedule for detemir in a basal-bolus regimen for type 1 diabetes is once-daily injection.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00117780.
Figures
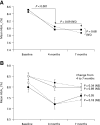
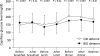

 , detemir at breakfast; ▪, detemir at bedtime. d, day.
, detemir at breakfast; ▪, detemir at bedtime. d, day.References
-
- Havelund S, Plum A, Ribel U, Jonassen I, Vølund A, Markussen J, Kurtzhals P: The mechanism of protraction of insulin detemir, a long-acting, acylated analog of human insulin. Pharm Res 21:1498–1504, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Plank J, Bodenlenz M, Sinner F, Magnes C, Görzer E, Regittnig W, Endahl LA, Draeger E, Zdravkovic M, Pieber TR: A double-blind, randomized, dose-response study investigating the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the long-acting insulin analog detemir. Diabetes Care 28:1107–1112, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Kurtzhals P: How to achieve a predictable basal insulin? Diabetes Metab 31(4 Pt 2):4S25–4S33, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Heise T, Nosek L, Rønn BB, Endahl L, Heinemann L, Kapitza C, Draeger E: Lower within-subject variability of insulin detemir in comparison to NPH insulin and insulin glargine in people with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 53:1614–1620, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Wutte A, Plank J, Bodenlenz M, Magnes C, Regittnig W, Sinner F, Rønn B, Zdravkovic M, Pieber TR: Proportional dose-response relationship and lower within-patient variability of insulin detemir and NPH insulin in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 115:461–467, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

