Increased expression of secreted frizzled-related protein 4 in polycystic kidneys
- PMID: 18945944
- PMCID: PMC2615724
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008040345
Increased expression of secreted frizzled-related protein 4 in polycystic kidneys
Abstract
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a common hereditary disease associated with progressive renal failure. Although cyst growth and compression of surrounding tissue may account for some loss of renal tissue, the other factors contributing to the progressive renal failure in patients with ADPKD are incompletely understood. Here, we report that secreted frizzled-related protein 4 (sFRP4) is upregulated in human ADPKD and in four different animal models of PKD, suggesting that sFRP4 expression is triggered by a common mechanism that underlies cyst formation. Cyst fluid from ADPKD kidneys activated the sFRP4 promoter and induced production of sFRP4 protein in renal tubular epithelial cell lines. Antagonism of the vasopressin 2 receptor blocked both promoter activity and tubular sFRP4 expression. In addition, sFRP4 selectively influenced members of the canonical Wnt signaling cascade and promoted cystogenesis of the zebrafish pronephros. sFRP4 was detected in the urine of both patients and animals with PKD, suggesting that sFRP4 may be a potential biomarker for monitoring the progression of ADPKD. Taken together, these observations suggest a potential role for SFRP4 in the pathogenesis of ADPKD.
Figures

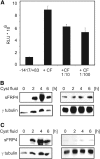

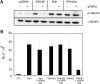

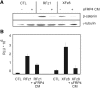

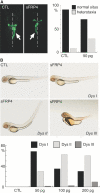
Similar articles
-
Polycystic kidney disease: pathogenesis and potential therapies.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Oct;1812(10):1337-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.11.014. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21146605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterisation of transcription factor profiles in polycystic kidney disease (PKD): identification and validation of STAT3 and RUNX1 in the injury/repair response and PKD progression.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Dec;97(12):1643-1656. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01852-3. Epub 2019 Nov 26. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31773180 Free PMC article.
-
Ouabain enhances renal cyst growth in a slowly progressive mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):F857-F869. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00056.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37823195 Free PMC article.
-
TAZ/Wnt-β-catenin/c-MYC axis regulates cystogenesis in polycystic kidney disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 17;117(46):29001-29012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009334117. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33122431 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ciliary trafficking of polycystin-2 and the pathogenesis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 Feb;35(2):93-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2010.02.001. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010. PMID: 20197605 Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt and planar cell polarity signaling in cystic renal disease.Organogenesis. 2014 Jan 1;10(1):86-95. doi: 10.4161/org.26766. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Organogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24162855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic ablation of sfrp4 in mice does not affect serum phosphate homeostasis.Endocrinology. 2011 May;152(5):2031-6. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1351. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21427221 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in kidney injury and repair: a double-edged sword.Lab Invest. 2016 Feb;96(2):156-67. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.153. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 26692289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental therapies and ongoing clinical trials to slow down progression of ADPKD.Curr Hypertens Rev. 2013 Feb;9(1):44-59. doi: 10.2174/1573402111309010008. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2013. PMID: 23971644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycystins and cellular Ca2+ signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Aug;70(15):2697-712. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1188-x. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23076254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grantham JJ: The etiology, pathogenesis, and treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Recent advances. Am J Kidney Dis 28: 788–803, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Wilson PD: Polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 350: 151–164, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Woo D: Apoptosis and loss of renal tissue in polycystic kidney diseases. N Engl J Med 333: 18–25, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Wilson PD: Epithelial cell polarity and disease. Am J Physiol 272: F434–F442, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Jones SE, Jomary C: Secreted Frizzled-related proteins: Searching for relationships and patterns. Bioessays 24: 811–820, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

