Side-chain recognition and gating in the ribosome exit tunnel
- PMID: 18946046
- PMCID: PMC2575457
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801795105
Side-chain recognition and gating in the ribosome exit tunnel
Abstract
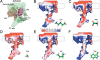
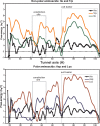
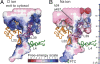
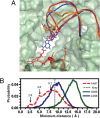
The ribosome is a large complex catalyst responsible for the synthesis of new proteins, an essential function for life. New proteins emerge from the ribosome through an exit tunnel as nascent polypeptide chains. Recent findings indicate that tunnel interactions with the nascent polypeptide chain might be relevant for the regulation of translation. However, the specific ribosomal structural features that mediate this process are unknown. Performing molecular dynamics simulations, we are studying the interactions between components of the ribosome exit tunnel and different chemical probes (specifically different amino acid side chains or monovalent inorganic ions). Our free-energy maps describe the physicochemical environment of the tunnel, revealing binding crevices and free-energy barriers for single amino acids and ions. Our simulations indicate that transport out of the tunnel could be different for diverse amino acid species. In addition, our results predict a notable protein-RNA interaction between a flexible 23S rRNA tetraloop (gate) and ribosomal protein L39 (latch) that could potentially obstruct the tunnel's exit. By relating our simulation data to earlier biochemical studies, we propose that ribosomal features at the exit of the tunnel can play a role in the regulation of nascent chain exit and ion flux. Moreover, our free-energy maps may provide a context for interpreting sequence-dependent nascent chain phenomenology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nakatogawa H, Ito K. The ribosomal exit tunnel functions as a discriminating gate. Cell. 2002;108:629–636. - PubMed
-
- Nakatogawa H, Ito K. Intraribosomal regulation of expression and fate of proteins. ChemBioChem. 2004;5:48–51. - PubMed
-
- Muto H, Nakatogawa H, Ito K. Genetically encoded but nonpolypeptide prolyl-tRNA functions in the A site for SecM-mediated ribosomal stall. Mol Cell. 2006;22:545–552. - PubMed
-
- Mankin AS. Nascent peptide in the “birth canal” of the ribosome. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:11–13. - PubMed
-
- Dresios J, Derkatch IL, Liebman SW, Synetos D. Yeast ribosomal protein L24 affects the kinetics of protein synthesis and ribosomal protein L39 improves translational accuracy, while mutants lacking both remain viable. Biochemistry. 2000;39:7236–7244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

