Acute respiratory distress syndrome in two rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta)
- PMID: 18947174
- PMCID: PMC2691537
Acute respiratory distress syndrome in two rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta)
Abstract
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is an important and potentially life-threatening complication in humans that arises subsequent to a variety of primary insults including noxious fume inhalation, infection, and trauma. Here we describe the first two cases of ARDS reported in association with postoperative complications in rhesus macaques. In agreement with the multifactorial nature of the human syndrome, ARDS in one monkey was attributed to sepsis, whereas in the other it was ascribed to neurogenic trauma. Despite the different etiologies, both monkeys demonstrated clinical features of ARDS, including progressive dyspnea and pulmonary edema, and syndrome-defining histopathologic criteria including edema with intraalveolar neutrophils, fibrinohemorrhagic effusions with crescentic membranes, and interstitial vascular degeneration. Recognition and aggressive treatment of ARDS at an early stage may improve survival rates in dyspneic nonhuman primates with underlying extrapulmonary diseases.
Figures
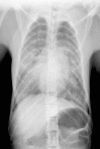
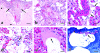
References
-
- Bergin IL, Chien CC, Marini RP, Fox JG. 2000. Isolation and characterization of Corynebacterium ulcerans from cephalic implants in macaques. Comp Med 50:530–535 - PubMed
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Flake K, Hudson L, Lamy M, LeGall JR, Morris A, Spragg R. 1994. Report of the American–European Consensus Conference on acute respiratory distress syndrome: definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. J Crit Care 9:72–81 - PubMed
-
- Carpenter JW. 2001. Exotic animal formulary, 3rd ed St Louis (MO): Elsevier Saunders
-
- Colt HG, Morris JF, Marston BJ, Sewell DL. 1991. Necrotizing tracheitis caused by Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum: unique case and review. Rev Infect Dis 13:73–76 - PubMed
-
- Davis LE. 1985. Handbook of small animal therapeutics. New York: Churchill Livingstone
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
