Polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 18947299
- PMCID: PMC2834200
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.med.60.101707.125712
Polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
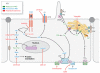
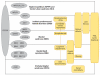
A number of inherited disorders result in renal cyst development. The most common form, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), is a disorder most often diagnosed in adults and caused by mutation in PKD1 or PKD2. The PKD1 protein, polycystin-1, is a large receptor-like protein, whereas polycystin-2 is a transient receptor potential channel. The polycystin complex localizes to primary cilia and may act as a mechanosensor essential for maintaining the differentiated state of epithelia lining tubules in the kidney and biliary tract. Elucidation of defective cellular processes has highlighted potential therapies, some of which are now being tested in clinical trials. ARPKD is the neonatal form of PKD and is associated with enlarged kidneys and biliary dysgenesis. The disease phenotype is highly variable, ranging from neonatal death to later presentation with minimal kidney disease. ARPKD is caused by mutation in PKHD1, and two truncating mutations are associated with neonatal lethality. The ARPKD protein, fibrocystin, is localized to cilia/basal body and complexes with polycystin-2. Rare, syndromic forms of PKD also include defects of the eye, central nervous system, digits, and/or neural tube and highlight the role of cilia and pathways such as Wnt and Hh in their pathogenesis.
Figures

References
LITERATURE CITED
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2007;369:1287–301. - PubMed
-
- Rossetti S, Harris PC. Genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007;18:1374–80. - PubMed
-
- Harris PC, Torres VE. GeneReviews; Genetic Diseases Online Reviews at Gene-Test-GeneClinics. Seattle; Univ. Washington: 2006. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=gene&part=pkd-ad.
-
- Grantham JJ, Torres VE, Chapman AB, et al. Volume progression in polycystic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:2122–30. - PubMed
-
- European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell. 1994;77:881–94. - PubMed
RELATED RESOURCES
-
- The PKD Foundation: http://www.pkdcure.org/
-
- The ARPKD Mutation Database: http://www.humgen.rwth-aachen.de/index.asp?subform=database.html& nav=database_nav.html.
-
- The ADPKD Mutation Database: http://pkdb.mayo.edu/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

