Systemic neutralizing antibodies induced by long interval mucosally primed systemically boosted immunization correlate with protection from mucosal SHIV challenge
- PMID: 18947849
- PMCID: PMC2723753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.09.016
Systemic neutralizing antibodies induced by long interval mucosally primed systemically boosted immunization correlate with protection from mucosal SHIV challenge
Abstract
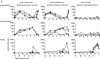
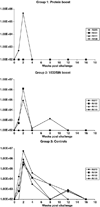
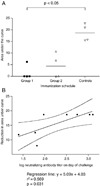
Immune correlates of vaccine protection from HIV-1 infection would provide important milestones to guide HIV-1 vaccine development. In a proof of concept study using mucosal priming and systemic boosting, the titer of neutralizing antibodies in sera was found to correlate with protection of mucosally exposed rhesus macaques from SHIV infection. Mucosal priming consisted of two sequential immunizations at 12-week intervals with replicating host range mutants of adenovirus type 5 (Ad5hr) expressing the HIV-1(89.6p) env gene. Following boosting with either heterologous recombinant protein or alphavirus replicons at 12-week intervals animals were intrarectally exposed to infectious doses of the CCR5 tropic SHIV(SF162p4). Heterologous mucosal prime systemic boost immunization elicited neutralizing antibodies (Nabs), antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC), and specific patterns of antibody binding to envelope peptides. Vaccine induced protection did not correlate with the type of boost nor T-cell responses, but rather with the Nab titer prior to exposure.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad A, Morisset R, Thomas R, Menezes J. Evidence for a defect of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic (ADCC) effector function and anti-HIV gp120/41-specific ADCC-mediating antibody titres in HIV-infected individuals. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1994;7(5):428–437. - PubMed
-
- Amara RR, Villinger F, Altman JD, Lydy SL, O’Neil SP, Staprans SI, Montefiori DC, Xu Y, Herndon JG, Wyatt LS, Candido MA, Kozyr NL, Earl PL, Smith JM, Ma HL, Grimm BD, Hulsey ML, Miller J, McClure HM, McNicholl JM, Moss B, Robinson HL. Control of a mucosal challenge and prevention of AIDS by a multiprotein DNA/MVA vaccine. Science. 2001;292(5514):69–74. - PubMed
-
- Barnett SW, Lu S, Srivastava I, Cherpelis S, Gettie A, Blanchard J, Wang S, Mboudjeka I, Leung L, Lian Y, Fong A, Buckner C, Ly A, Hilt S, Ulmer J, Wild CT, Mascola JR, Stamatatos L. The ability of an oligomeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope antigen to elicit neutralizing antibodies against primary HIV-1 isolates is improved following partial deletion of the second hypervariable region. J Virol. 2001;75(12):5526–5540. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertley FM, Kozlowski PA, Wang SW, Chappelle J, Patel J, Sonuyi O, Mazzara G, Montefiori D, Carville A, Mansfield KG, Aldovini A. Control of simian/human immunodeficiency virus viremia and disease progression after IL-2-augmented DNA-modified vaccinia virus Ankara nasal vaccination in nonhuman primates. J Immunol. 2004;172(6):3745–3757. - PubMed
-
- Bogers WM, Niphuis H, ten Haaft P, Laman JD, Koornstra W, Heeney JL. Protection from HIV-1 envelope-bearing chimeric simian immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) in rhesus macaques infected with attenuated SIV: consequences of challenge. Aids. 1995;9(12):F13–F18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

