HGVbaseG2P: a central genetic association database
- PMID: 18948288
- PMCID: PMC2686551
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn748
HGVbaseG2P: a central genetic association database
Abstract
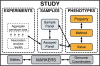
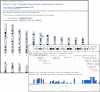
The Human Genome Variation database of Genotype to Phenotype information (HGVbaseG2P) is a new central database for summary-level findings produced by human genetic association studies, both large and small. Such a database is needed so that researchers have an easy way to access all the available association study data relevant to their genes, genome regions or diseases of interest. Such a depository will allow true positive signals to be more readily distinguished from false positives (type I error) that fail to consistently replicate. In this paper we describe how HGVbaseG2P has been constructed, and how its data are gathered and organized. We present a range of user-friendly but powerful website tools for searching, browsing and visualizing G2P study findings. HGVbaseG2P is available at http://www.hgvbaseg2p.org.
Figures
References
-
- Shields PG. Publication bias is a scientific problem with adverse ethical outcomes: the case for a section for null results. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2000;9:771–772. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi RE. Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Allen NC, Bagade S, McQueen MB, Ioannidis JPA, Kavvoura FK, Khoury MJ, Tanzi RE, Bertram L. Systematic meta-analyses and field synopsis of genetic association studies in schizophrenia: the SzGene database. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:827–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

