Active involvement of Robo1 and Robo4 in filopodia formation and endothelial cell motility mediated via WASP and other actin nucleation-promoting factors
- PMID: 18948384
- PMCID: PMC4048916
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.07-098269
Active involvement of Robo1 and Robo4 in filopodia formation and endothelial cell motility mediated via WASP and other actin nucleation-promoting factors
Abstract
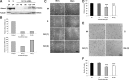
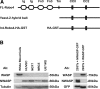
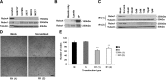
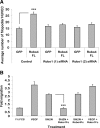
This study aimed to further elucidate the function of Roundabout proteins in endothelium. We show that both Robo1 and Robo4 are present in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and have knocked expression down using small interfering RNA (siRNA) technology. Roundabout knockout endothelial cells were then studied in a variety of in vitro assays. We also performed a yeast 2-hybrid analysis using the intracellular domain of Robo4 as bait to identify interacting proteins and downstream signaling. Both Robo1 and Robo4 siRNA knockdown and transfection of Robo4-green fluorescent protein inhibited endothelial cell movement and disrupted tube formation on Matrigel. Consistent with a role in regulating cell movement, yeast 2-hybrid and glutathione-S-transferase pulldown analyses show Robo4 binding to a Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP), neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, and WASP-interacting protein actin-nucleating complex. We have further shown that Robo1 forms a heterodimeric complex with Robo4, and that transfection of Robo4GFP into HUVECs induces filopodia formation. We finally show using Robo1 knockdown cells that Robo1 is essential for Robo4-mediated filopodia induction. Our results favor a model whereby Slit2 binding to a Robo1/Robo4 heterodimer activates actin nucleation-promoting factors to promote endothelial cell migration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functionally defining the endothelial transcriptome, from Robo4 to ECSCR.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Dec;37(Pt 6):1214-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0371214. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19909249
-
Suppression of Slit2/Robo1 mediated HUVEC migration by Robo4.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jan 22;469(4):797-802. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.075. Epub 2015 Dec 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26713366
-
Silencing of directional migration in roundabout4 knockdown endothelial cells.BMC Cell Biol. 2008 Nov 3;9:61. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-9-61. BMC Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18980679 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ROBO4 signalling in developmental and pathological angiogenesis.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:683025. doi: 10.1155/2014/683025. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24689049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shear stress, tip cells and regulators of endothelial migration.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Dec;39(6):1571-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20110746. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 22103489 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Slit/Robo Signaling Pathway.J Cancer. 2019 Jun 2;10(12):2694-2705. doi: 10.7150/jca.31877. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31258778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Slit-Robo signalling in heart development.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 May 1;114(6):794-804. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy061. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29538649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Slit-Robo signaling in the regulation of tissue barriers.Tissue Barriers. 2017 Apr 3;5(2):e1331155. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2017.1331155. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Tissue Barriers. 2017. PMID: 28598714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of Robo4 and their effects on angiogenesis.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jul 10;39(7):BSR20190513. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190513. Print 2019 Jul 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31160487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid rafts: integrated platforms for vascular organization offering therapeutic opportunities.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Apr;72(8):1537-57. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1814-x. Epub 2015 Jan 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25552244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seeger M., Tear G., Ferres-Marco D., Goodman C. S. Mutations affecting growth cone guidance in Drosophila: genes necessary for guidance toward or away from the midline. Neuron. 1993;10:409–426. - PubMed
-
- Kidd T., Brose K., Mitchell K. J., Fetter R. D., Tessier-Lavigne M., Goodman C. S., Tear G. Roundabout controls axon crossing of the CNS midline and defines a novel subfamily of evolutionarily conserved guidance receptors. Cell. 1998;92:205–215. - PubMed
-
- Huminiecki L., Gorn M., Suchting S., Poulsom R., Bicknell R. Magic Roundabout is a new member of the Roundabout receptor family that is endothelial specific and expressed at sites of active angiogenesis. Genomics. 2002;79:547–552. - PubMed
-
- Legg J. A., Herbert J. M. J., Clissold P., Bicknell R. Slits and Roundabouts in cancer, tumour angiogenesis and endothelial cell migration. Angiogenesis. 2008;11:13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

