Dscam guides embryonic axons by Netrin-dependent and -independent functions
- PMID: 18948420
- PMCID: PMC2712571
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.023739
Dscam guides embryonic axons by Netrin-dependent and -independent functions
Abstract
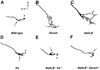
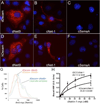
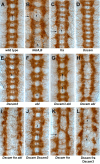
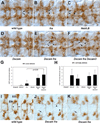
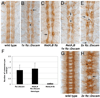
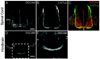
Developing axons are attracted to the CNS midline by Netrin proteins and other as yet unidentified signals. Netrin signals are transduced in part by Frazzled (Fra)/DCC receptors. Genetic analysis in Drosophila indicates that additional unidentified receptors are needed to mediate the attractive response to Netrin. Analysis of Bolwig's nerve reveals that Netrin mutants have a similar phenotype to Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule (Dscam) mutants. Netrin and Dscam mutants display dose sensitive interactions, suggesting that Dscam could act as a Netrin receptor. We show using cell overlay assays that Netrin binds to fly and vertebrate Dscam, and that Dscam binds Netrin with the same affinity as DCC. At the CNS midline, we find that Dscam and its paralog Dscam3 act redundantly to promote midline crossing. Simultaneous genetic knockout of the two Dscam genes and the Netrin receptor fra produces a midline crossing defect that is stronger than the removal of Netrin proteins, suggesting that Dscam proteins also function in a pathway parallel to Netrins. Additionally, overexpression of Dscam in axons that do not normally cross the midline is able to induce ectopic midline crossing, consistent with an attractive receptor function. Our results support the model that Dscam proteins function as attractive receptors for Netrin and also act in parallel to Frazzled/DCC. Furthermore, the results suggest that Dscam proteins have the ability to respond to multiple ligands and act as receptors for an unidentified midline attractive cue. These functions in axon guidance have implications for the pathogenesis of Down Syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Agarwala KL, Nakamura S, Tsutumi Y, Yamakawa K. Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule DSCAM mediates homophilic intercellular adhesion. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000;79:118–126. - PubMed
-
- Agarwala KL, Ganesh S, Amano K, Suzuki T, Yamakawa K. DSCAM, a highly conserved gene in mammals, expressed in differentiating mouse brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001;281:697–705. - PubMed
-
- Barlow GM, Chen XN, Shi ZY, Lyons GE, Kurnit DM, Celle L, Spinner NB, Zackai E, Pettenati MJ, Van Riper AJ, et al. Down syndrome congenital heart disease: a narrowed region and a candidate gene. Genet. Med. 2001;3:91–101. - PubMed
-
- Barlow GM, Micales B, Chen XN, Lyons GE, Korenberg JR. Mammalian DSCAMs: roles in the development of the spinal cord, cortex, and cerebellum? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;293:881–891. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw GJ, Kidd T, Murray D, Pawson T, Goodman CS. Repulsive axon guidance: Abelson and Enabled play opposing roles downstream of the roundabout receptor. Cell. 2000;101:703–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

