Cytokine-mediated regulation of antimicrobial proteins
- PMID: 18949018
- PMCID: PMC2901862
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2433
Cytokine-mediated regulation of antimicrobial proteins
Abstract
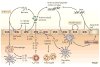
Antimicrobial proteins constitute a phylogenetically ancient form of innate immunity that provides host defence at skin and mucosal surfaces. Although some components of this system are constitutively expressed, new evidence reviewed in this Progress article shows that the production of certain antimicrobial proteins by epithelial cells can also be regulated by cytokines of the innate and adaptive immune systems. In particular, the effector cytokines interleukin-17 and interleukin-22, which are produced by the T-helper-17-cell subset, are emerging as crucial regulators of antimicrobial-peptide production in the gut and the lungs. This suggests that this T-cell lineage and its cytokines have important roles in skin and mucosal immunity.
Figures

References
-
- Zelensky AN, Gready JE. The C-type lectin-like domain superfamily. FEBS J. 2005;272:6179–6217. - PubMed
-
- Soruri A, Grigat J, Forssmann U, Riggert J, Zwirner J. β-defensins chemoattract macrophages and mast cells but not lymphocytes and dendritic cells: CCR6 is not involved. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:2474–2486. - PubMed
-
- Kuhara T, Yamauchi K, Tamura Y, Okamura H. Oral administration of lactoferrin increases NK cell activity in mice via increased production of IL-18 and type I IFN in the small intestine. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006;26:489–499. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, et al. Host defense peptide LL-37, in synergy with inflammatory mediator IL-1β, augments immune responses by multiple pathways. J Immunol. 2007;179:7684–7691. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, et al. Cathelicidin LL-37 induces the generation of reactive oxygen species and release of human α-defensins from neutrophils. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:1124–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

