Lipid rafts and caveolae in signaling by growth factor receptors
- PMID: 18949068
- PMCID: PMC2570545
- DOI: 10.2174/1874091X00701010012
Lipid rafts and caveolae in signaling by growth factor receptors
Abstract
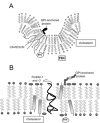
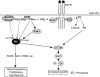
Lipid rafts and caveolae are microdomains of the plasma membrane enriched in sphingolipids and cholesterol, and hence are less fluid than the remainder of the membrane. Caveolae have an invaginated structure, while lipid rafts are flat regions of the membrane. The two types of microdomains have different protein compositions (growth factor receptors and their downstream molecules) suggesting that lipid rafts and caveolae have a role in the regulation of signaling by these receptors. The purpose of this review is to discuss this model, and the implications that it might have regarding a potential role for lipid rafts and caveolae in human cancer. Particular attention will be paid to the epidermal growth factor receptor, for which the largest amount of information is available. It has been proposed that caveolins act as tumor suppressors. The role of lipid rafts is less clear, but they seem to be capable of acting as 'signaling platforms', in which signal initiation and propagation can occur efficiently.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Methods for the study of signaling molecules in membrane lipid rafts and caveolae.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;332:181-91. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-048-0:181. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16878693
-
Lipid rafts, caveolae, and epidermal growth factor receptor family: friends or foes?Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 11;22(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01876-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39394159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid rafts, caveolae, and their endocytosis.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010;282:135-63. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)82003-9. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20630468 Review.
-
Caveolae and lipid rafts: G protein-coupled receptor signaling microdomains in cardiac myocytes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1047:166-72. doi: 10.1196/annals.1341.015. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16093494 Review.
-
The differential protein and lipid compositions of noncaveolar lipid microdomains and caveolae.Cell Res. 2009 Apr;19(4):497-506. doi: 10.1038/cr.2009.27. Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19255590
Cited by
-
Rafting Down the Metastatic Cascade: The Role of Lipid Rafts in Cancer Metastasis, Cell Death, and Clinical Outcomes.Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;81(1):5-17. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2199. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 32999001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progesterone receptor membrane component 1 regulates lipid homeostasis and drives oncogenic signaling resulting in breast cancer progression.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 13;22(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01312-8. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32660617 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-IR internalizes with Caveolin-1 and PTRF/Cavin in HaCat cells.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 30;5(11):e14157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014157. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21152401 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin alpha1beta1 regulates epidermal growth factor receptor activation by controlling peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-dependent caveolin-1 expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jun;30(12):3048-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00892-09. Epub 2010 Apr 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20368353 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of β1 integrins and caveolin-1 by TF/FVIIa promotes IGF-1R signaling and cell survival.Apoptosis. 2020 Aug;25(7-8):519-534. doi: 10.1007/s10495-020-01611-7. Apoptosis. 2020. PMID: 32458278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed SN, Brown DA, London E. Biochemistry. 1997;36:10944–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
