Carotid Body AT(4) Receptor Expression and its Upregulation in Chronic Hypoxia
- PMID: 18949084
- PMCID: PMC2570565
- DOI: 10.2174/1874192400701010001
Carotid Body AT(4) Receptor Expression and its Upregulation in Chronic Hypoxia
Abstract
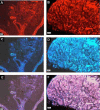
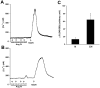
Hypoxia regulates the local expression of angiotensin-generating system in the rat carotid body and the me-tabolite angiotensin IV (Ang IV) may be involved in the modulation of carotid body function. We tested the hypothesis that Ang IV-binding angiotensin AT(4) receptors play a role in the adaptive change of the carotid body in hypoxia. The expression and localization of Ang IV-binding sites and AT(4) receptors in the rat carotid bodies were studied with histochemistry. Specific fluorescein-labeled Ang IV binding sites and positive staining of AT(4) immunoreactivity were mainly found in lobules in the carotid body. Double-labeling study showed the AT(4) receptor was localized in glomus cells containing tyrosine hydroxylase, suggesting the expression in the chemosensitive cells. Intriguingly, the Ang IV-binding and AT(4) immunoreactivity were more intense in the carotid body of chronically hypoxic (CH) rats (breathing 10% oxygen for 4 weeks) than the normoxic (Nx) control. Also, the protein level of AT(4) receptor was doubled in the CH comparing with the Nx group, supporting an upregulation of the expression in hypoxia. To examine if Ang IV induces intracellular Ca(2+) response in the carotid body, cytosolic calcium ([Ca(2+)](i)) was measured by spectrofluorimetry in fura-2-loaded glomus cells dissociated from CH and Nx carotid bodies. Exogenous Ang IV elevated [Ca(2+)](i) in the glomus cells and the Ang IV response was significantly greater in the CH than the Nx group. Hence, hypoxia induces an upregulation of the expression of AT(4) receptors in the glomus cells of the carotid body with an increase in the Ang IV-induced [Ca(2+)]i elevation. This may be an additional pathway enhancing the Ang II action for the activation of chemoreflex in the hypoxic response during chronic hypoxia.
Keywords: Angiotensin IV; angiotensin IV receptor; chemoreceptor; type-I cells.
Figures


References
-
- Gonzalez C, Almaraz L, Obeso A, Rigual R. Carotid body chemoreceptors: from natural stimuli to sensory discharges. Physiol Rev. 1994;74:829–98. - PubMed
-
- Lahiri S, Rozanov C, Roy A, Storey B, Buerk DG. Regulation of oxygen sensing in peripheral arterial chemoreceptors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;33:755–74. - PubMed
-
- Dasso LL, Buckler KJ, Vaughan-Jones RD. Interactions between hypoxia and hypercapnic acidosis on calcium signaling in carotid body type I cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;279:L36–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
