Calculation of left ventricular relaxation time constant-Tau in patients with aortic regurgitation by continuous-wave Doppler
- PMID: 18949095
- PMCID: PMC2570579
- DOI: 10.2174/1874192400802010028
Calculation of left ventricular relaxation time constant-Tau in patients with aortic regurgitation by continuous-wave Doppler
Abstract
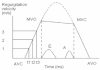
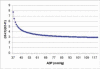
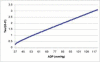
Left ventricular relaxation time constant, Tau, is the best index to evaluate left ventricular diastolic function. The measurement is only available traditionally in catheter lab. In Echo lab, several methods of non-invasive measurement of Tau have been tried since 1992, however almost all the methods are still utilizing the same formula to calculate Tau as in catheter lab, which makes them inconvenient, time-consuming and sometimes not very accurate. A simple method to calculate Tau in patients with mitral regurgitation has been developed just based on Weiss' formula and simplified Bernoulli's equation. Similarly, formulas are developed here by pure mathematical derivative to calculate Tau by continuous-wave Doppler in patients with aortic regurgitation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calculation of left ventricular relaxation time constant-Tau in humans by continuous-wave Doppler.Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2008;2:9-11. doi: 10.2174/1874192400802010009. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2008. PMID: 18949092 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive assessment of left ventricular relaxation using continuous-wave Doppler aortic regurgitant velocity curve. Its comparative value to the mitral regurgitation method.Circulation. 1995 Jan 1;91(1):192-200. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.1.192. Circulation. 1995. PMID: 7805202
-
Continuous wave Doppler echocardiography for noninvasive assessment of left ventricular dP/dt and relaxation time constant from mitral regurgitant spectra in patients.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Mar 15;23(4):970-6. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90645-9. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994. PMID: 8106704
-
[Non-invasive evaluation of the hemodynamic profile in patients with heart failure: estimation of left atrial pressure].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2000 Oct;1(10):1326-33. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11068716 Review. Italian.
-
Newer Doppler measures of left ventricular diastolic function.Clin Cardiol. 1996 Apr;19(4):277-88. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960190402. Clin Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8706367 Review.
Cited by
-
Time constants of cardiac function and their calculations.Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2010 Aug 9;4:168-72. doi: 10.2174/1874192401004010168. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2010. PMID: 21160911 Free PMC article.
-
Calculation of left ventricular diastolic time constant (Tau) in dogs with aortic regurgitation using continuous-wave Doppler spectra.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2021 Apr 28;18(4):252-260. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2021.04.007. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33995504 Free PMC article.
-
Symmetry of cardiac function assessment.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2016 Sep;13(6):517-20. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2016.06.014. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27582768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C, Rodriguez L, Levine RA, Weyman AE, Thomas JD. Noninvasive measurement of the time constant of left ventricular relaxation using the continuous-wave Doppler velocity profile of mitral regurgitation. Circulation. 1992;86:272–78. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura RA, Schwartz RS, Tajik AJ, Holmes DR Jr. Noninvasive measurement of rate of left ventricular relaxation by Doppler Echocardiography.Validation with simultaneous cardiac catheterization. Circulation. 1993;88:146–55. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Rodriguez L, Lethor JP, et al. Continuous wave Doppler echocardiography for noninvasive assessment of the left ventricular dP/dt and relaxation time constant from mitral regurgitant spectra in patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994;23:970–76. - PubMed
-
- Scalia GM, Greenberg NL, McCarthy PM, Thomas JD, Vandervoort PM. Noninvasive assessment of the ventricular relaxation time constant in humans by Doppler Echocardiography. Circulation. 1997;95:151–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
