uPA/uPAR downregulation inhibits radiation-induced migration, invasion and angiogenesis in IOMM-Lee meningioma cells and decreases tumor growth in vivo
- PMID: 18949356
- PMCID: PMC2575644
uPA/uPAR downregulation inhibits radiation-induced migration, invasion and angiogenesis in IOMM-Lee meningioma cells and decreases tumor growth in vivo
Abstract
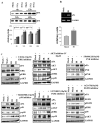
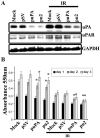
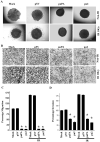
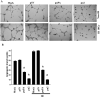
Meningioma is a well-known tumor of the central nervous system, and is treated by surgical resection and/or radiation. Recently, ionizing radiation has been shown to enhance invasiveness of surviving tumor cells, and several proteolytic enzyme molecules, including urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), seem to be upregulated after radiation. uPA and its receptor (uPAR) have been strongly implicated in tumor invasion, angiogenesis and progression. Hence, the tumor-associated uPA-uPAR system is considered a potential target for cancer therapy. In the present study, we show that radiation increases uPA levels in the IOMM-Lee meningioma cells, and subsequently, increases tumor invasion, migration and angiogenesis in vitro. Studies with signaling molecule inhibitors AG1478, U0126 and SB203580 (specific inhibitors of EGFR, MEK1/2 and p38 respectively) showed inhibition of uPA levels in both basal and irradiated-IOMM-Lee cells. The PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) and the AKT inhibitor (AKT inhibitor IV) also partially decreased uPA expression, whereas SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, did not affect uPA levels in either radiated or non-radiated cells. Further, a bicistronic plasmid construct with small interfering RNA (siRNA) against uPA and its receptor inhibited tumor invasion, migration and angiogenesis in radiation-treated IOMM-Lee cells. In addition, siRNA against uPA and its receptor inhibited subcutaneous tumor growth in athymic nude mice in combination with radiation in a synergistic manner. Thus, the specific targeting of proteases via RNA interference could augment the therapeutic effect of radiation and prevent the adverse effects resulting from tumor cells that receive sublethal doses of radiation within the tumor mass.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiation-inducible silencing of uPA and uPAR in vitro and in vivo in meningioma.Int J Oncol. 2010 Apr;36(4):809-16. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000557. Int J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20198323 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference-mediated targeting of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression in the IOMM-lee malignant meningioma cell line inhibits tumor growth, tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis.Int J Oncol. 2007 Jul;31(1):5-17. Int J Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17549400 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic role of p53 is suppressed by si-RNA bicistronic construct of uPA, uPAR and cathepsin-B in meningiomas both in vitro and in vivo.Int J Oncol. 2011 Apr;38(4):973-83. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.934. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Int J Oncol. 2011. Retraction in: Int J Oncol. 2021 Apr;58(4):6. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5186. PMID: 21290090 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Mechanism of tumor cell-induced extracellular matrix degradation--inhibition of cell-surface proteolytic activity might have a therapeutic effect on tumor cell invasion and metastasis].Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Aug;48(8):623-32. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8808830 Review. Japanese.
-
VEGF-initiated angiogenesis and the uPA/uPAR system.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Nov-Dec;6(6):535-615. doi: 10.4161/cam.22243. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 23076133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Patient-Derived Orthotopic Xenograft (PDOX) Mouse Models of Primary and Recurrent Meningioma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 5;12(6):1478. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061478. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517016 Free PMC article.
-
Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and/or matrix metalloproteinase-9 inhibition induces apoptosis signaling through lipid rafts in glioblastoma xenograft cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Sep;9(9):2605-17. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0245. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20716639 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of uPA and uPAR blocks radiation-induced MCP-1 mediated recruitment of endothelial cells in meningioma.Cell Signal. 2011 Aug;23(8):1299-310. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.03.011. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21426933 Free PMC article.
-
uPA and uPAR shRNA inhibit angiogenesis via enhanced secretion of SVEGFR1 independent of GM-CSF but dependent on TIMP-1 in endothelial and glioblastoma cells.Mol Oncol. 2012 Feb;6(1):33-47. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2011.11.008. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Mol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22177802 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting inflammatory pathways for tumor radiosensitization.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):1904-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.039. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599771 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bondy M, Ligon BL. Epidemiology and etiology of intracranial meningiomas: a review. J Neurooncol. 1996;29:197–205. - PubMed
-
- Modha A, Gutin PH. Diagnosis and treatment of atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: a review. Neurosurgery. 2005;57:538–550. - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith B, McDermott MW. Meningioma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2006;17:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Ko KW, Nam DH, Kong DS, Lee JI, Park K, Kim JH. Relationship between malignant subtypes of meningioma and clinical outcome. J Clin Neurosci. 2007;14:747–753. - PubMed
-
- Valerie K, Yacoub A, Hagan MP, Curiel DT, Fisher PB, Grant S, Dent P. Radiation-induced cell signaling: inside-out and outside-in. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:789–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS061835/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS47699/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057529/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA075557/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS57529/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA 75557/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 92393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047699/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS61835/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA 95058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116708/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 116708/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

