The aldo-keto reductase superfamily and its role in drug metabolism and detoxification
- PMID: 18949601
- PMCID: PMC2663408
- DOI: 10.1080/03602530802431439
The aldo-keto reductase superfamily and its role in drug metabolism and detoxification
Abstract
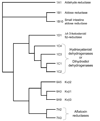
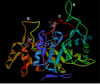
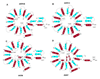
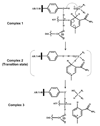
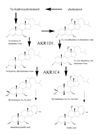
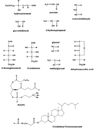
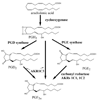
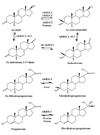
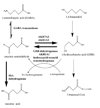
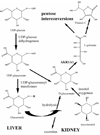
The aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily comprises enzymes that catalyze redox transformations involved in biosynthesis, intermediary metabolism, and detoxification. Substrates of AKRs include glucose, steroids, glycosylation end-products, lipid peroxidation products, and environmental pollutants. These proteins adopt a (beta/alpha)(8) barrel structural motif interrupted by a number of extraneous loops and helixes that vary between proteins and bring structural identity to individual families. The human AKR family differs from the rodent families. Due to their broad substrate specificity, AKRs play an important role in the phase II detoxification of a large number of pharmaceuticals, drugs, and xenobiotics.
Figures

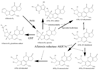
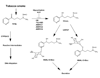
References
-
- Aimond F, Kwak SP, Rhodes KJ, Nerbonne JM. Accessory kv beta 1 subunits differentially modulate the functional expression of voltage-gated K+ channels in mouse ventricular myocytes. Circulation Research. 2005;96:451–458. - PubMed
-
- Atalla A, Breyer-Pfaff U, Maser E. Purification and characterization of oxidoreductases-catalyzing carbonyl reduction of the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-methylnitrosamino-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) in human liver cytosol. Xenobiotica. 2000;30:755–769. - PubMed
-
- Atalla A, Maser E. Characterization of enzymes participating in carbonyl reduction of 4-methylnitrosamino-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) in human placenta. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 2001;130:737–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
