Axonal transport and the delivery of pre-synaptic components
- PMID: 18950710
- PMCID: PMC2653082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.10.003
Axonal transport and the delivery of pre-synaptic components
Abstract
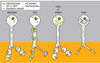
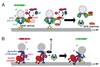
The mechanisms for delivering components to nerve terminals are diverse and highly regulated. The diversity of kinesin motors alone is insufficient to account for the specificity of delivery. Additional specificity and control are contributed by adaptor proteins and associated regulatory molecules. The interaction of cargos with these complexes can confer distinct behaviors on the transport of synaptic organelles. The rich regulatory mechanisms of transport that are only now emerging as the cargo-motor complexes are defined and subsequent local events that regulate their dynamic relationship are examined. Here we review recent studies of kinesin-related axonal transport of three crucial synaptic components, Piccolo-bassoon Transport Vesicles (PTVs), Synaptic Vesicle Precursors (SVPs), and mitochondria, and the mechanisms that modulate their transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest with the publication of this article.
Figures
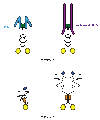

References
-
- De Vos KJ, Grierson AJ, Ackerley S, Miller CC. Role of Axonal Transport in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2008;31:151–173. - PubMed
-
- Stokin GB, Goldstein LS. Axonal transport and Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:607–627. - PubMed
-
- Saxena S, Caroni P. Mechanisms of axon degeneration: from development to disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2007;83:174–191. - PubMed
-
- Schaefer AM, Sanes JR, Lichtman JW. A compensatory subpopulation of motor neurons in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Comp Neurol. 2005;490:209–219. - PubMed
-
- Ibanez CF. Message in a bottle: long-range retrograde signaling in the nervous system. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:519–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

