Young and older good learners have higher levels of brain nicotinic receptor binding
- PMID: 18950900
- PMCID: PMC2858226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.09.002
Young and older good learners have higher levels of brain nicotinic receptor binding
Abstract
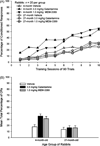
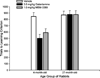
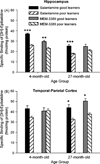
Neuronal alphabeta heteromeric and alpha7 homomeric nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) were compared in 4- and 27-month rabbits selected for learning proficiency. Sixty 4- and 60 27-month rabbits received the alpha7 nAChR agonist (MEM-3389), galantamine, or vehicle during training in trace eyeblink classical conditioning. Brain tissue from the best and worst young and older learners was analyzed with radioligand binding. Vehicle-treated 4- and 27-month good learners had higher alphabeta heteromeric nAChR binding in hippocampus and temporal-parietal cortex than poor learners, and this result was replicated in both age groups of rabbits treated with galantamine. Results indicate that anatomically more numerous nAChRs or functional activation of a greater number of nAChRs may characterize animals demonstrating optimal learning. During normal aging the expression of high-affinity binding sites declines. Age-related changes in the expression of hippocampal alphabeta heteromeric nAChRs may account for some of the documented age-related impairment in learning. However, individual differences in alphabeta heteromeric nAChRs also exist early in life, as better learning in 4-month rabbits was associated with significantly higher binding.
Copyright 2008 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Birtsch C, Wevers A, Traber J, Maelicke A, Bloch W, Schröder H. Expression of α4-1 and α5 nicotinic cholinoceptor mRNA in the aging rat cerebral cortex. Neurobiol. Aging. 1997;18:335–342. - PubMed
-
- Changeux JP, Bertrand D, Corringer PJ, Dehaene S, Edelstein S, Lena C, Le Novere N, Marubio L, Picciotto M, Zoli M. Brain nicotinic receptors: structure and regulation, role in learning and reinforcement. Brain Res. Rev. 1998;26:198–216. - PubMed
-
- Chein JM, Schneider W. Neuroimaging studies of practice-related change: fMRI and meta-analytic evidence of a domain-general control network for learning. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 2005;25:607–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

