A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of milk oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy
- PMID: 18951617
- PMCID: PMC3764488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.09.030
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of milk oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy
Abstract
Background: Orally administered, food-specific immunotherapy appears effective in desensitizing and potentially permanently tolerizing allergic individuals.
Objective: We sought to determine whether milk oral immunotherapy (OIT) is safe and efficacious in desensitizing children with cow's milk allergy.
Methods: Twenty children were randomized to milk or placebo OIT (2:1 ratio). Dosing included 3 phases: the build-up day (initial dose, 0.4 mg of milk protein; final dose, 50 mg), daily doses with 8 weekly in-office dose increases to a maximum of 500 mg, and continued daily maintenance doses for 3 to 4 months. Double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenges; end-point titration skin prick tests; and milk protein serologic studies were performed before and after OIT.
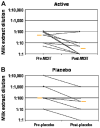
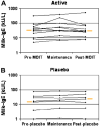
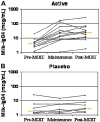
Results: Nineteen patients, 6 to 17 years of age, completed treatment: 12 in the active group and 7 in the placebo group. One dropped out because of persistent eczema during dose escalation. Baseline median milk IgE levels in the active (n = 13) versus placebo (n = 7) groups were 34.8 kUa/L (range, 4.86-314 kUa/L) versus 14.6 kUa/L (range, 0.93-133.4 kUa/L). The median milk threshold dose in both groups was 40 mg at the baseline challenge. After OIT, the median cumulative dose inducing a reaction in the active treatment group was 5140 mg (range 2540-8140 mg), whereas all patients in the placebo group reacted at 40 mg (P = .0003). Among 2437 active OIT doses versus 1193 placebo doses, there were 1107 (45.4%) versus 134 (11.2%) total reactions, with local symptoms being most common. Milk-specific IgE levels did not change significantly in either group. Milk IgG levels increased significantly in the active treatment group, with a predominant milk IgG4 level increase.
Conclusions: Milk OIT appears to be efficacious in the treatment of cow's milk allergy. The side-effect profile appears acceptable but requires further study.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest: The rest of the authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sampson HA. Food allergy. Part 2: diagnosis and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:981–9. - PubMed
-
- Sicherer SH, Furlong TJ, Munoz-Furlong A, Burks AW, Sampson HA. A voluntary registry for peanut and tree nut allergy: characteristics of the first 5149 registrants. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:128–32. - PubMed
-
- Vander Leek TK, Liu AH, Stefanski K, Blacker B, Bock SA. The natural history of peanut allergy in young children and its association with serum peanut-specific IgE. J Pediatr. 2000;137:749–55. - PubMed
-
- Yu JW, Kagan R, Verreault N, Nicolas N, Joseph L, St Pierre Y, et al. Accidental ingestions in children with peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118:466–72. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001-2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1016–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

