The motion aftereffect reloaded
- PMID: 18951829
- PMCID: PMC3087115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2008.09.002
The motion aftereffect reloaded
Abstract
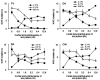
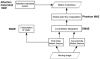
The motion aftereffect is a robust illusion of visual motion resulting from exposure to a moving pattern. There is a widely accepted explanation of it in terms of changes in the response of cortical direction-selective neurons. Research has distinguished several variants of the effect. Converging recent evidence from different experimental techniques (psychophysics, single-unit recording, brain imaging, transcranial magnetic stimulation, visual evoked potentials and magnetoencephalography) reveals that adaptation is not confined to one or even two cortical areas, but occurs at multiple levels of processing involved in visual motion analysis. A tentative motion-processing framework is described, based on motion aftereffect research. Recent ideas on the function of adaptation see it as a form of gain control that maximises the efficiency of information transmission at multiple levels of the visual pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Anstis SM, Verstraten FAJ, Mather G. The motion aftereffect: a review. Trends in Cognitive Science. 1998;2:111–117. - PubMed
-
- Mather G, Verstraten FA, Anstis S. The Motion After-Effect. MIT Press; 1998.
-
- Sutherland NS. Figural aftereffects and apparent size. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology. 1961;13:222–228.
-
- Barlow HB, Hill RM. Selective sensitivity to direction of movement in ganglion cells of the rabbit retina. Science. 1963;139:412–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

