T cell-derived lymphotoxin regulates liver regeneration
- PMID: 18952083
- PMCID: PMC3060763
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.015
T cell-derived lymphotoxin regulates liver regeneration
Abstract
Background & aims: The ability of the liver to regenerate hepatic mass is essential to withstanding liver injury. The process of liver regeneration is tightly regulated by distinct signaling cascades involving components of the innate immune system, cytokines, and growth factors. However, the role of the adaptive immune system in regulation of liver regeneration is not well-defined. The role of adaptive immune system in liver regeneration was investigated in lymphocyte-deficient mice and in conditional lymphotoxin-deficient mice.
Methods: A model of liver regeneration after 70% partial hepatectomy was used, followed by examination of liver pathology, survival, DNA synthesis, and cytokine expression.
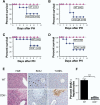
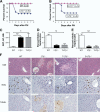
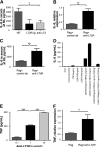
Results: We found that mice deficient in T cells show a reduced capacity for liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy. Furthermore, surface lymphotoxin, provided by T cells, is critical for liver regeneration. Mice specifically deficient in T-cell lymphotoxin had increased liver damage and a reduced capacity to initiate DNA synthesis after partial hepatectomy. Transfer of splenocytes from wild-type but not lymphotoxin-deficient mice improved liver regeneration in T cell-deficient mice. We found that an agonistic antibody against the lymphotoxin beta receptor was able to facilitate liver regeneration by reducing liver injury, increasing interleukin-6 production, hepatocyte DNA synthesis, and survival of lymphocyte-deficient (Rag) mice after partial hepatectomy.
Conclusions: The adaptive immune system directly regulates liver regeneration via a T cell-derived lymphotoxin axis, and pharmacological stimulation of lymphotoxin beta receptor might represent a novel therapeutic approach to improve liver regeneration.
Figures



References
-
- Taub R. Liver regeneration: from myth to mechanism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:836–847. - PubMed
-
- Fausto N, Campbell JS, Riehle KJ. Liver regeneration. Hepatology. 2006;43:S45–S53. - PubMed
-
- Seki E, Tsutsui H, Iimuro Y, et al. Contribution of Toll-like receptor/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling to murine liver regeneration. Hepatology. 2005;41:443–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 DK067187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK042086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK081417/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080736/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58897/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI062026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK067187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081417/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA115540/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL007237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058897/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA115540/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK42086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

