The shape of human navigation: how environmental geometry is used in maintenance of spatial orientation
- PMID: 18952206
- PMCID: PMC2612041
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cognition.2008.09.001
The shape of human navigation: how environmental geometry is used in maintenance of spatial orientation
Abstract
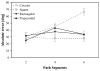
The role of environmental geometry in maintaining spatial orientation was measured in immersive virtual reality using a spatial updating task (requiring maintenance of orientation during locomotion) within rooms varying in rotational symmetry (the number of room orientations providing the same perspective). Spatial updating was equally good in trapezoidal, rectangular and square rooms (one-fold, two-fold and four-fold rotationally symmetric, respectively) but worse in a circular room (infinity-fold rotationally symmetric). This contrasts with reorientation performance, which was incrementally impaired by increasing rotational symmetry. Spatial updating performance in a shape-changing room (containing visible corners and flat surfaces, but changing its shape over time) was no better than performance in a circular room, indicating that superior spatial updating performance in angular environments was due to remembered room shape, rather than improved self-motion perception in the presence of visible corners and flat surfaces.
Figures


References
-
- Chance SS. How we use sensory information to keep oriented as we locomote. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of California; Santa Barbara: 2000.
-
- Cheng K. A purely geometric module in the rat’s spatial representation. Cognition. 1986;23:149–178. - PubMed
-
- Cheng K, Gallistel CR. Shape parameters explain data from spatial transformations: Comment on Pearce et al. (2004) and Tommasi and Polli (2004) Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 2005;31(2):254–259. - PubMed
-
- Cheng K, Newcombe NS. Is there a geometric module for spatial orientation? Squaring theory and evidence. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review. 2005;12(1):1–23. - PubMed
-
- Cheng K, Shettleworth SJ, Huttenlocher J, Rieser JJ. Bayesian integration of spatial information. Psychological Bulletin. 2007;133:625–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

