Mutations of LRTOMT, a fusion gene with alternative reading frames, cause nonsyndromic deafness in humans
- PMID: 18953341
- PMCID: PMC3404732
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.245
Mutations of LRTOMT, a fusion gene with alternative reading frames, cause nonsyndromic deafness in humans
Abstract
Many proteins necessary for sound transduction have been identified through positional cloning of genes that cause deafness. We report here that mutations of LRTOMT are associated with profound nonsyndromic hearing loss at the DFNB63 locus on human chromosome 11q13.3-q13.4. LRTOMT has two alternative reading frames and encodes two different proteins, LRTOMT1 and LRTOMT2, detected by protein blot analyses. LRTOMT2 is a putative methyltransferase. During evolution, new transcripts can arise through partial or complete coalescence of genes. We provide evidence that in the primate lineage LRTOMT evolved from the fusion of two neighboring ancestral genes, which exist as separate genes (Lrrc51 and Tomt) in rodents.
Figures


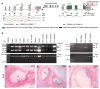
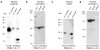
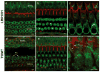
Comment in
-
LRTOMT: a new tone in understanding the symphony of non-syndromic deafness.Clin Genet. 2009 Mar;75(3):227-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2009.01150_3.x. Clin Genet. 2009. PMID: 19250379 No abstract available.
References
-
- Friedman TB, Griffith AJ. Human nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2003;4:341–402. - PubMed
-
- Grant L, Fuchs PA. Auditory transduction in the mouse. Pflugers Arch. 2007;454:793–804. - PubMed
-
- Morton CC, Nance WE. Newborn hearing screening--a silent revolution. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2151–64. - PubMed
-
- Pasek S, Risler JL, Brezellec P. Gene fusion/fission is a major contributor to evolution of multi-domain bacterial proteins. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:1418–23. - PubMed
-
- Kalay E, et al. A novel locus for autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment, DFNB63, maps to chromosome 11q13.2–q13.4. J Mol Med. 2007;85:397–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

