Reconstitution of ThiC in thiamine pyrimidine biosynthesis expands the radical SAM superfamily
- PMID: 18953358
- PMCID: PMC2587053
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.121
Reconstitution of ThiC in thiamine pyrimidine biosynthesis expands the radical SAM superfamily
Abstract
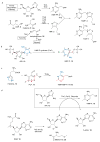
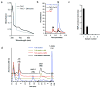
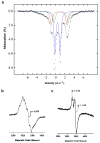
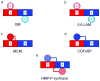
4-Amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P) synthase catalyzes a complex rearrangement of 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (AIR) to form HMP-P, the pyrimidine moiety of thiamine phosphate. We determined the three-dimensional structures of HMP-P synthase and its complexes with the product HMP-P and a substrate analog imidazole ribotide. The structure of HMP-P synthase reveals a homodimer in which each protomer comprises three domains: an N-terminal domain with a novel fold, a central (betaalpha)(8) barrel and a disordered C-terminal domain that contains a conserved CX(2)CX(4)C motif, which is suggestive of a [4Fe-4S] cluster. Biochemical studies have confirmed that HMP-P synthase is iron sulfur cluster-dependent, that it is a new member of the radical SAM superfamily and that HMP-P and 5'-deoxyadenosine are products of the reaction. Mössbauer and EPR spectroscopy confirm the presence of one [4Fe-4S] cluster. Structural comparisons reveal that HMP-P synthase is homologous to a group of adenosylcobalamin radical enzymes. This similarity supports an evolutionary relationship between these two superfamilies.
Figures

References
-
- Begley TP, et al. Thiamin biosynthesis in prokaryotes. Arch Microbiol. 1999;171:293–300. - PubMed
-
- Settembre E, Begley TP, Ealick SE. Structural biology of enzymes of the thiamin biosynthesis pathway. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13:739–747. - PubMed
-
- Jurgenson CT, Chatterjee A, Begley TP, Ealick SE. Structural Insights into the Function of the Thiamin Biosynthetic Enzyme Thi4 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 2006;45:11061–11070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- PubChem-Substance/56269940
- PubChem-Substance/56269941
- PubChem-Substance/56269942
- PubChem-Substance/56269943
- PubChem-Substance/56269944
- PubChem-Substance/56269945
- PubChem-Substance/56269946
- PubChem-Substance/56269947
- PubChem-Substance/56269948
- PubChem-Substance/56269949
- PubChem-Substance/56269950
- PubChem-Substance/56269951
- PubChem-Substance/56269952
- PubChem-Substance/56269953
- PubChem-Substance/56269954
- PubChem-Substance/56269955
- PubChem-Substance/56269956
- PubChem-Substance/56269957
- PubChem-Substance/56269958
- PubChem-Substance/56269959
- PubChem-Substance/56269960
- PubChem-Substance/56269961
- PubChem-Substance/56269962
- PubChem-Substance/56269963
- PubChem-Substance/56269964
- PubChem-Substance/56269965
- PubChem-Substance/56269966
- PubChem-Substance/56269967
- PubChem-Substance/56269968
- PubChem-Substance/56269969
- PubChem-Substance/56269970
- PubChem-Substance/56269971
- PubChem-Substance/56269972
- PubChem-Substance/56269973
- PubChem-Substance/56269974
- PubChem-Substance/56269975
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

